COPYRIGHT; LIST OF PUBLICATIONS ................................ ii
FOREWORD ...................................................... iii
PREFACE; ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ...................................... iii
Chapter 1
J. CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY of the RHOMBOHEDRAL CARBONATES
Richard J. Reeder
INTRODUCTION .................................................... 1
RHOMBOHEDRAL VERSUS HEXAGONAL AXIAL SYSTEMS ..................... 2
THE CO3 GROUP AS A STRUCTURAL UNIT .............................. 4
THE 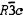 CARBONATES .............................................. 6
The calcite structure ........................................ 6
Calcite isotypes ............................................. 8
Atomic thermal vibrations ................................ 10
Structural variation ..................................... 14
Solid solutions of CARBONATES .............................................. 6
The calcite structure ........................................ 6
Calcite isotypes ............................................. 8
Atomic thermal vibrations ................................ 10
Structural variation ..................................... 14
Solid solutions of 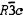 carbonates ........................... 17
The magnesian calcite solid solution ..................... 17
The CaCO3-CdCO3 solid solution ........................... 20
The Ni-Mg carbonate solid solution ....................... 20
Lattice parameters in other solid solutions ................. 21
THE carbonates ........................... 17
The magnesian calcite solid solution ..................... 17
The CaCO3-CdCO3 solid solution ........................... 20
The Ni-Mg carbonate solid solution ....................... 20
Lattice parameters in other solid solutions ................. 21
THE 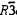 CARBONATES .............................................. 22
The dolomite structure ...................................... 22
Interatomic distances .................................... 23
Octahedral distortion .................................... 26
Thermal parameters ....................................... 28
Dolomite isotypes ........................................... 28
Ankerite and ferroan dolomite ............................ 28
Kutnahorite .............................................. 31
Other transition metal dolomites ......................... 31
Calcian dolomites and ankerites ............................. 32
Cation order in dolomite-structure carbonates ............... 32
Thermal disordering ...................................... 32
Structural changes ....................................... 35
Disorder in low-temperature dolomites .................... 35
Lattice parameters of dolomite-type carbonates .............. 37
OTHER DOUBLE CARBONATES ........................................ 40
CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY AT HIGH TEMPERATURES AND PRESSURES ........... 43
Thermal expansion ........................................... 43
High-temperature transformations of calcite ................. 45
CaCO3(II) structure ......................................... 45
SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK .................................... 46
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ................................................ 47
Chapter 2
PHASE RELATIONS of RHOMBOHEDRAL CARBONATES
Julian R. Goldsmith
INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS .......................... 49
THE END-MEMBER CARBONATES ...................................... 51
DOLOMITE-TYPE COMPOUNDS ........................................ 51
BINARY PHASE RELATIONS ......................................... 51
CaCO3-MgCO3 ................................................. 51
Relations at moderate pressures .......................... 51
Relations at higher pressures and temperatures ........... 55
Additional considerations in subsolidus relations ........ 58
CdCO3-MgCO3 ................................................. 60
CaCO3-MnCO3 ................................................. 60
CaCO3-FeCO3 ................................................. 62
Additional binary joins with a single solvus ................ 63
CaCO3-NiCO3; СаСO3-СоСO3; MgCO3-NiCO3 .................... 63
Binary joins with extensive solid solubility ................ 64
The join CaCO3-ZnCO3 and Zn-dolomite ......................... 64
A note on the asymmetry of the solvi ........................ 65
TERNARY PHASE RELATIONS ........................................ 66
CaCO3-MgCO3-FeCO3 ............................................ 66
CaCO3-MgCO3-MnCO3 ............................................ 70
Order-disorder relations in Fe- and Mn-containing
dolomites ................................................... 70
The systems CaCO3-MgCO3-CoCO3 and CaCO3-MgCO3-NiCO3 .......... 72
SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK .................................... 75
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ................................................ 76
Chapter 3
SOLID SOLUTIONS and SOLVI among METAMORPHIC CARBONATES
with APPLICATIONS to GEOLOGIC THERMOBAROMETRY
Eric 3. Essene
INTRODUCTION ................................................... 77
EXPERIMENTAL DATA BASE ......................................... 77
DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE COMPOSITIONS ........................ 78
COMPOSITIONS OF METAMORPHIC CARBONATES ......................... 80
Rhombohedral carbonates ..................................... 81
Orthorhombic carbonates ..................................... 84
SOLVUS LIMITS IN METAMORPHIC CARBONATES ........................ 85
Solvi in the system CaCO3-MgCO3-FeCO3 ....................... 85
Solvi in the system CaCO3-MgCO3-MnCO3 ....................... 86
APPLICATIONS OF CALCITE-DOLOMITE THERMOMETRY ................... 88
Regional metamorphic rocks .................................. 89
Contact metamorphic rocks ................................... 91
THE ARAGONITE-CALCITE TRANSITION AS A THERMOBAROMETER .......... 93
COEXISTING ORTHORHOMBIC AND RHOMBOHEDRAL CARBONATES ............ 94
SUGGESTIONS FOR FURTHER WORK ................................... 95
SUMMARY ........................................................ 95
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ................................................ 96
Chapter 4
MAGNESIAN CALCITES: LOW-TEMPERATURE OCCURRENCE,
SOLUBILITY and SOLID-SOLUTION BEHAVIOR
Fred T. Mackenzie, William D. Bischoff, Finley C. Bishop,
Michele Loijens, Jane Schoonmaker & Roland Wollast
INTRODUCTION ................................................... 97
LOW-TEMPERATURE OCCURRENCE ..................................... 98
Skeletal magnesian calcites ................................. 98
Magnesian calcite cement .................................... 98
UNIT CELL PARAMETERS: BIOGENIC AND SYNTHETIC INORGANIC
PHASES ........................................................ 104
High-temperature synthetic materials ....................... 104
Synthesis techniques .................................... 104
Unit cell parameters .................................... 105
Low-temperature synthetic materials ........................ 107
Biogenic materials ......................................... 108
SOLUBILITIES AND SOLID SOLUTION BEHAVIOR ................... 112
Solubilities of magnesian calcites ......................... 114
Dissolution experiments ................................. 114
Precipitation experiments ............................... 118
Interpretation of experimental data ..................... 118
Theoretical considerations ................................. 119
Thermodynamic equilibrium ............................... 120
Stoichiometric saturation ............................... 124
Experimental tests of stoichiometric saturation ......... 126
Expression of solubility ................................ 127
Evaluation of thermodynamic properties from dissolution
experiments ................................................ 129
Other approaches to estimation of magnesian calcite
properties ................................................. 132
Solid solution properties ............................... 132
Estimation of free energy of mixing from high-
temperature data ........................................ 135
Estimation of excess lattice energy .................... 136
Evaluation of the heat of mixing by calorimetric
measurements ............................................ 138
Hypothesis of an hydrated magnesian calcite ................ 140
SOME CONCLUDING REMARKS ....................................... 142
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 144
Chapter 5
CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY and PHASE RELATIONS of ORTHORHOMBIC
CARBONATES
J. Alexander Speer
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 145
CRYSTALLOGRAPHY ............................................... 145
Crystal structures ......................................... 145
Charge distribution ........................................ 150
ACO3 polymorphism ......................................... 151
Twinning ................................................... 152
Morphology ................................................. 152
The CaBa(CO3)2 phases ...................................... 154
Carbocernaite .............................................. 157
CHEMISTRY ..................................................... 158
Inorganic orthorhombic carbonates .......................... 158
Biogenic orthorhombic carbonates ........................... 161
Recent shells ........................................... 161
Fossil shells ........................................... 167
IS0T0PIC COMPOSITION .......................................... 169
Dependence on crystal chemistry ............................ 170
Dependence on physical conditions .......................... 170
Dependence on source ....................................... 171
PHASE RELATIONS ............................................... 171
Unary systems .............................................. 171
Binary systems ............................................. 173
CaCO3-SrCO3 ............................................. 173
СаСO3-BаСO3 ............................................. 174
СаCO3-РbCO3 ............................................. 174
SrСO3-ВаСO3 ............................................. 174
SrCO3-PbCO3 ............................................. 175
BaCO3-PbCO3 ............................................. 175
Ternary systems ............................................ 176
Phase relations in aqueous systems ......................... 177
Phase relations involving noncarbonate minerals ............ 178
OCCURRENCE OF ORTHORHOMBIC CARBONATES AND DISCUSSION OF
THEIR COMPOSITIONS AND MINERAL ASSEMBLAGES .................... 178
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ........................................... 182
Density .................................................... 182
Lattice parameters ......................................... 184
Optical properties ......................................... 185
Luminescence ............................................... 188
Magnetic properties ........................................ 188
Infrared and Raman spectra ................................. 188
SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK ................................... 189
Chapter 6
POLYMORPHS of CaCO3 and the ARAGONITE-CALCITE
TRANSFORMATION
William D. Carlson
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 191
THE POLYMORPHS OF CALCIUM CARBONATE ........................... 191
The calcite-aragonite equilibrium ......................... 193
CaCO3(II) and CaCO3(III) ................................... 195
CaCO3(IV) and CaCO3(V) ..................................... 196
The role of rotational disorder of CO3 groups .............. 198
Evidence for disordering ................................ 198
Possible disordering schemes ............................ 200
Speculations on disorder in CaCO3 as a function of
pressure and temperature ................................ 201
ARAGONITE-CALCITE TRANSFORMATIONS IN THE SOLID STATE ........ 202
The calcite-to-aragonite transformation ................... 202
The transformation under conditions of aragonite
stability ............................................... 202
The transformation outside the aragonite stability
field ................................................... 203
The aragonite-to-calcite transformation ................... 203
Petrographic observations ............................... 204
Experiments measuring bulk transformation rates ......... 204
Independent determination of growth rates ............... 207
Extraction of nucleation rates from bulk
transformation rates .................................... 207
Summary ................................................. 209
THE ARAGONITE-CALCITE TRANSFORMATION IN THE PRESENCE OF
WATER ......................................................... 211
Observational evidence for the nature of the aqueous
transformation ............................................. 212
Marine environments ..................................... 212
Fresh water environments ................................ 212
Mechanisms of the transformation ......................... 213
Dissolution at surface of parent crystal ................ 214
Nucleation of product crystal ........................... 214
Transport of complexes in solution ...................... 214
Precipitation at surface of product crystal ............. 214
Interpretation of natural occurrences in terms of
reaction mechanisms ........................................ 215
Reasons for extremely limited extent of transformation
in sea water ............................................ 215
Reasons for apparent differences in transformation
type .................................................... 215
Reasons for oriented overgrowths and topotaxial
replacement ............................................. 217
Reasons for selective transformation of skeletal
materials ............................................... 218
Reasons for long-term preservation in ancient
limestone ............................................... 218
Experimental attempts to quantify reaction kinetics ....... 219
The significance of transport processes ................. 219
The time dependence of the overall transformation ....... 219
Inconsistency of a time-squared volume dependence with
other observations ...................................... 220
A possible explanation for the time-squared volume
dependence .............................................. 222
CONCLUSIONS AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR FURTHER RESEARCH .......... 224
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 225
Chapter 7
The KINETICS of CALCIUM CARBONATE DISSOLUTION and
PRECIPITATION
John W. Morse
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 227
BASIC PRINCIPLES .............................................. 228
REACTION KINETICS IN SIMPLE SOLUTIONS ......................... 231
Dissolution ................................................ 231
General observations .................................... 231
Models and mechanisms ................................... 234
Precipitation .............................................. 238
General observations and models ......................... 238
Secondary nucleation .................................... 239
DISSOLUTION AND PRECIPITATION REACTIONS OF NONBIOGENIC
CARBONATES IN COMPLEX SOLUTIONS ............................... 241
General considerations ..................................... 241
Major influences ........................................ 241
Models for reacting surfaces and inhibitors ............. 242
Individual seawater-component influences ................... 244
Magnesium ............................................... 244
Sulphate ................................................ 246
Reaction kinetics in seawater and related solutions ........ 246
Dissolution ............................................. 246
Precipitation ........................................... 247
Other specific influences .................................. 249
Phosphates .............................................. 249
Heavy metals ............................................ 252
Organics ................................................ 253
SPECIFIC TOPICS ............................................. 254
Biogenic carbonate dissolution kinetics .................... 254
General considerations .................................. 254
Influence of grain size ................................. 256
Prediction of solubility from kinetics .................. 258
Kinetic influence on coprecipitation reactions ............. 261
Experimental methods .................................... 261
Cation coprecipitation with calcite ..................... 262
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 264
Chapter 8
TRACE ELEMENTS and ISOTOPES in SEDIMENTARY CARBONATES
Ján Veizer
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 265
INCORPORATION OF TRACE ELEMENTS INTO CARBONATE MINERALS ....... 267
INCORPORATION OF STABLE ISOTOPES OF OXYGEN AND CARBON INTO
CARBONATE MINERALS ............................................ 271
Theoretically predicted composition of carbonate
minerals ................................................... 272
Isotopic variations in natural waters ...................... 276
Isotopic composition of natural carbonates ................. 278
INCORPORATION OF RADIOGENIC ISOTOPES INTO CARBONATE
MINERALS ...................................................... 279
Radiocarbon ................................................ 279
U-series disequilibrium nuclei ............................. 282
Isotopes of strontium ...................................... 284
DIAGENETIC REPARTITIONING OF TRACERS .......................... 285
RECORD OF TERRESTRIAL EVOLUTION IN ANCIENT CARBONATES ......... 288
Oxygen isotope paleothermometry ............................ 289
Post-Triassic paleoceanography ............................. 289
Carbon isotopes of ancient oceans: the story of life ....... 292
Strontium isotopes and buffering of the oceans ............. 294
Oxygen isotopic composition of sedimentary carbonates ...... 296
Secular variations in chemical composition of carbonates ... 298
CONCLUDING REMARKS ............................................ 299
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 300
Chapter 9
MICROSTRUCTURES in CARBONATES
Hans-Rudolf Wenk, David J. Barber & Richard J. Reeder
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 301
ORIGINS OF MICROSTRUCTURES .................................... 303
Deformation microstructures ................................ 303
Transformation microstructures ............................. 306
Growth microstructures ..................................... 311
Dislocations ............................................ 311
Growth bands ............................................ 311
Faults .................................................. 313
Stacking disorder ....................................... 313
Twins ................................................... 313
METHODS OF ANALYSIS ........................................... 313
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) ......................... 314
Transmission electron microscopy (ТЕМ) ..................... 315
Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) ........... 317
High resolution electron microscopy (HREM) ................. 318
POLYMORPHIC TRANSFORMATIONS ................................... 319
Cation ordering in dolomite ................................ 319
Aragonite → calcite transformation ......................... 321
Observations in sedimentary rocks ....................... 322
Observations of the solid state transformation in the
ТЕМ ..................................................... 326
VARIATIONS IN STACKING ORDER .................................. 328
Periodic basal superstructure in dolomite .................. 328
Stacking disorder and polytypes in rare earth carbonates ... 329
MODULATED STRUCTURES PARALLEL TO r = {1014} .................. 332
Calcian dolomites .......................................... 332
Saddle dolomites ........................................... 338
Calcite .................................................... 343
Carbonatites ............................................... 344
Interpretation ............................................. 348
OTHER SEDIMENTARY CARBONATES .................................. 352
Recent dolomites ........................................... 352
Magnesian calcites ......................................... 352
DEFORMATION ................................................... 354
Deformation mechanisms ..................................... 354
Calcite ................................................. 355
Dolomite ................................................ 356
The effects of twinning .................................... 357
Biaxiality .............................................. 359
Other defects in deformed carbonates ....................... 359
Dislocations ............................................ 359
Stacking faults ......................................... 360
Stylolites - "Pressure solution" ........................ 364
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 367
REFERENCES .................................................... 369
APPENDIX
A partial list of some noteworthy papers that have
appeared since the first printing .......................... 395 CARBONATES .............................................. 22
The dolomite structure ...................................... 22
Interatomic distances .................................... 23
Octahedral distortion .................................... 26
Thermal parameters ....................................... 28
Dolomite isotypes ........................................... 28
Ankerite and ferroan dolomite ............................ 28
Kutnahorite .............................................. 31
Other transition metal dolomites ......................... 31
Calcian dolomites and ankerites ............................. 32
Cation order in dolomite-structure carbonates ............... 32
Thermal disordering ...................................... 32
Structural changes ....................................... 35
Disorder in low-temperature dolomites .................... 35
Lattice parameters of dolomite-type carbonates .............. 37
OTHER DOUBLE CARBONATES ........................................ 40
CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY AT HIGH TEMPERATURES AND PRESSURES ........... 43
Thermal expansion ........................................... 43
High-temperature transformations of calcite ................. 45
CaCO3(II) structure ......................................... 45
SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK .................................... 46
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ................................................ 47
Chapter 2
PHASE RELATIONS of RHOMBOHEDRAL CARBONATES
Julian R. Goldsmith
INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS .......................... 49
THE END-MEMBER CARBONATES ...................................... 51
DOLOMITE-TYPE COMPOUNDS ........................................ 51
BINARY PHASE RELATIONS ......................................... 51
CaCO3-MgCO3 ................................................. 51
Relations at moderate pressures .......................... 51
Relations at higher pressures and temperatures ........... 55
Additional considerations in subsolidus relations ........ 58
CdCO3-MgCO3 ................................................. 60
CaCO3-MnCO3 ................................................. 60
CaCO3-FeCO3 ................................................. 62
Additional binary joins with a single solvus ................ 63
CaCO3-NiCO3; СаСO3-СоСO3; MgCO3-NiCO3 .................... 63
Binary joins with extensive solid solubility ................ 64
The join CaCO3-ZnCO3 and Zn-dolomite ......................... 64
A note on the asymmetry of the solvi ........................ 65
TERNARY PHASE RELATIONS ........................................ 66
CaCO3-MgCO3-FeCO3 ............................................ 66
CaCO3-MgCO3-MnCO3 ............................................ 70
Order-disorder relations in Fe- and Mn-containing
dolomites ................................................... 70
The systems CaCO3-MgCO3-CoCO3 and CaCO3-MgCO3-NiCO3 .......... 72
SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK .................................... 75
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ................................................ 76
Chapter 3
SOLID SOLUTIONS and SOLVI among METAMORPHIC CARBONATES
with APPLICATIONS to GEOLOGIC THERMOBAROMETRY
Eric 3. Essene
INTRODUCTION ................................................... 77
EXPERIMENTAL DATA BASE ......................................... 77
DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE COMPOSITIONS ........................ 78
COMPOSITIONS OF METAMORPHIC CARBONATES ......................... 80
Rhombohedral carbonates ..................................... 81
Orthorhombic carbonates ..................................... 84
SOLVUS LIMITS IN METAMORPHIC CARBONATES ........................ 85
Solvi in the system CaCO3-MgCO3-FeCO3 ....................... 85
Solvi in the system CaCO3-MgCO3-MnCO3 ....................... 86
APPLICATIONS OF CALCITE-DOLOMITE THERMOMETRY ................... 88
Regional metamorphic rocks .................................. 89
Contact metamorphic rocks ................................... 91
THE ARAGONITE-CALCITE TRANSITION AS A THERMOBAROMETER .......... 93
COEXISTING ORTHORHOMBIC AND RHOMBOHEDRAL CARBONATES ............ 94
SUGGESTIONS FOR FURTHER WORK ................................... 95
SUMMARY ........................................................ 95
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ................................................ 96
Chapter 4
MAGNESIAN CALCITES: LOW-TEMPERATURE OCCURRENCE,
SOLUBILITY and SOLID-SOLUTION BEHAVIOR
Fred T. Mackenzie, William D. Bischoff, Finley C. Bishop,
Michele Loijens, Jane Schoonmaker & Roland Wollast
INTRODUCTION ................................................... 97
LOW-TEMPERATURE OCCURRENCE ..................................... 98
Skeletal magnesian calcites ................................. 98
Magnesian calcite cement .................................... 98
UNIT CELL PARAMETERS: BIOGENIC AND SYNTHETIC INORGANIC
PHASES ........................................................ 104
High-temperature synthetic materials ....................... 104
Synthesis techniques .................................... 104
Unit cell parameters .................................... 105
Low-temperature synthetic materials ........................ 107
Biogenic materials ......................................... 108
SOLUBILITIES AND SOLID SOLUTION BEHAVIOR ................... 112
Solubilities of magnesian calcites ......................... 114
Dissolution experiments ................................. 114
Precipitation experiments ............................... 118
Interpretation of experimental data ..................... 118
Theoretical considerations ................................. 119
Thermodynamic equilibrium ............................... 120
Stoichiometric saturation ............................... 124
Experimental tests of stoichiometric saturation ......... 126
Expression of solubility ................................ 127
Evaluation of thermodynamic properties from dissolution
experiments ................................................ 129
Other approaches to estimation of magnesian calcite
properties ................................................. 132
Solid solution properties ............................... 132
Estimation of free energy of mixing from high-
temperature data ........................................ 135
Estimation of excess lattice energy .................... 136
Evaluation of the heat of mixing by calorimetric
measurements ............................................ 138
Hypothesis of an hydrated magnesian calcite ................ 140
SOME CONCLUDING REMARKS ....................................... 142
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 144
Chapter 5
CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY and PHASE RELATIONS of ORTHORHOMBIC
CARBONATES
J. Alexander Speer
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 145
CRYSTALLOGRAPHY ............................................... 145
Crystal structures ......................................... 145
Charge distribution ........................................ 150
ACO3 polymorphism ......................................... 151
Twinning ................................................... 152
Morphology ................................................. 152
The CaBa(CO3)2 phases ...................................... 154
Carbocernaite .............................................. 157
CHEMISTRY ..................................................... 158
Inorganic orthorhombic carbonates .......................... 158
Biogenic orthorhombic carbonates ........................... 161
Recent shells ........................................... 161
Fossil shells ........................................... 167
IS0T0PIC COMPOSITION .......................................... 169
Dependence on crystal chemistry ............................ 170
Dependence on physical conditions .......................... 170
Dependence on source ....................................... 171
PHASE RELATIONS ............................................... 171
Unary systems .............................................. 171
Binary systems ............................................. 173
CaCO3-SrCO3 ............................................. 173
СаСO3-BаСO3 ............................................. 174
СаCO3-РbCO3 ............................................. 174
SrСO3-ВаСO3 ............................................. 174
SrCO3-PbCO3 ............................................. 175
BaCO3-PbCO3 ............................................. 175
Ternary systems ............................................ 176
Phase relations in aqueous systems ......................... 177
Phase relations involving noncarbonate minerals ............ 178
OCCURRENCE OF ORTHORHOMBIC CARBONATES AND DISCUSSION OF
THEIR COMPOSITIONS AND MINERAL ASSEMBLAGES .................... 178
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ........................................... 182
Density .................................................... 182
Lattice parameters ......................................... 184
Optical properties ......................................... 185
Luminescence ............................................... 188
Magnetic properties ........................................ 188
Infrared and Raman spectra ................................. 188
SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK ................................... 189
Chapter 6
POLYMORPHS of CaCO3 and the ARAGONITE-CALCITE
TRANSFORMATION
William D. Carlson
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 191
THE POLYMORPHS OF CALCIUM CARBONATE ........................... 191
The calcite-aragonite equilibrium ......................... 193
CaCO3(II) and CaCO3(III) ................................... 195
CaCO3(IV) and CaCO3(V) ..................................... 196
The role of rotational disorder of CO3 groups .............. 198
Evidence for disordering ................................ 198
Possible disordering schemes ............................ 200
Speculations on disorder in CaCO3 as a function of
pressure and temperature ................................ 201
ARAGONITE-CALCITE TRANSFORMATIONS IN THE SOLID STATE ........ 202
The calcite-to-aragonite transformation ................... 202
The transformation under conditions of aragonite
stability ............................................... 202
The transformation outside the aragonite stability
field ................................................... 203
The aragonite-to-calcite transformation ................... 203
Petrographic observations ............................... 204
Experiments measuring bulk transformation rates ......... 204
Independent determination of growth rates ............... 207
Extraction of nucleation rates from bulk
transformation rates .................................... 207
Summary ................................................. 209
THE ARAGONITE-CALCITE TRANSFORMATION IN THE PRESENCE OF
WATER ......................................................... 211
Observational evidence for the nature of the aqueous
transformation ............................................. 212
Marine environments ..................................... 212
Fresh water environments ................................ 212
Mechanisms of the transformation ......................... 213
Dissolution at surface of parent crystal ................ 214
Nucleation of product crystal ........................... 214
Transport of complexes in solution ...................... 214
Precipitation at surface of product crystal ............. 214
Interpretation of natural occurrences in terms of
reaction mechanisms ........................................ 215
Reasons for extremely limited extent of transformation
in sea water ............................................ 215
Reasons for apparent differences in transformation
type .................................................... 215
Reasons for oriented overgrowths and topotaxial
replacement ............................................. 217
Reasons for selective transformation of skeletal
materials ............................................... 218
Reasons for long-term preservation in ancient
limestone ............................................... 218
Experimental attempts to quantify reaction kinetics ....... 219
The significance of transport processes ................. 219
The time dependence of the overall transformation ....... 219
Inconsistency of a time-squared volume dependence with
other observations ...................................... 220
A possible explanation for the time-squared volume
dependence .............................................. 222
CONCLUSIONS AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR FURTHER RESEARCH .......... 224
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 225
Chapter 7
The KINETICS of CALCIUM CARBONATE DISSOLUTION and
PRECIPITATION
John W. Morse
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 227
BASIC PRINCIPLES .............................................. 228
REACTION KINETICS IN SIMPLE SOLUTIONS ......................... 231
Dissolution ................................................ 231
General observations .................................... 231
Models and mechanisms ................................... 234
Precipitation .............................................. 238
General observations and models ......................... 238
Secondary nucleation .................................... 239
DISSOLUTION AND PRECIPITATION REACTIONS OF NONBIOGENIC
CARBONATES IN COMPLEX SOLUTIONS ............................... 241
General considerations ..................................... 241
Major influences ........................................ 241
Models for reacting surfaces and inhibitors ............. 242
Individual seawater-component influences ................... 244
Magnesium ............................................... 244
Sulphate ................................................ 246
Reaction kinetics in seawater and related solutions ........ 246
Dissolution ............................................. 246
Precipitation ........................................... 247
Other specific influences .................................. 249
Phosphates .............................................. 249
Heavy metals ............................................ 252
Organics ................................................ 253
SPECIFIC TOPICS ............................................. 254
Biogenic carbonate dissolution kinetics .................... 254
General considerations .................................. 254
Influence of grain size ................................. 256
Prediction of solubility from kinetics .................. 258
Kinetic influence on coprecipitation reactions ............. 261
Experimental methods .................................... 261
Cation coprecipitation with calcite ..................... 262
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 264
Chapter 8
TRACE ELEMENTS and ISOTOPES in SEDIMENTARY CARBONATES
Ján Veizer
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 265
INCORPORATION OF TRACE ELEMENTS INTO CARBONATE MINERALS ....... 267
INCORPORATION OF STABLE ISOTOPES OF OXYGEN AND CARBON INTO
CARBONATE MINERALS ............................................ 271
Theoretically predicted composition of carbonate
minerals ................................................... 272
Isotopic variations in natural waters ...................... 276
Isotopic composition of natural carbonates ................. 278
INCORPORATION OF RADIOGENIC ISOTOPES INTO CARBONATE
MINERALS ...................................................... 279
Radiocarbon ................................................ 279
U-series disequilibrium nuclei ............................. 282
Isotopes of strontium ...................................... 284
DIAGENETIC REPARTITIONING OF TRACERS .......................... 285
RECORD OF TERRESTRIAL EVOLUTION IN ANCIENT CARBONATES ......... 288
Oxygen isotope paleothermometry ............................ 289
Post-Triassic paleoceanography ............................. 289
Carbon isotopes of ancient oceans: the story of life ....... 292
Strontium isotopes and buffering of the oceans ............. 294
Oxygen isotopic composition of sedimentary carbonates ...... 296
Secular variations in chemical composition of carbonates ... 298
CONCLUDING REMARKS ............................................ 299
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 300
Chapter 9
MICROSTRUCTURES in CARBONATES
Hans-Rudolf Wenk, David J. Barber & Richard J. Reeder
INTRODUCTION .................................................. 301
ORIGINS OF MICROSTRUCTURES .................................... 303
Deformation microstructures ................................ 303
Transformation microstructures ............................. 306
Growth microstructures ..................................... 311
Dislocations ............................................ 311
Growth bands ............................................ 311
Faults .................................................. 313
Stacking disorder ....................................... 313
Twins ................................................... 313
METHODS OF ANALYSIS ........................................... 313
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) ......................... 314
Transmission electron microscopy (ТЕМ) ..................... 315
Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) ........... 317
High resolution electron microscopy (HREM) ................. 318
POLYMORPHIC TRANSFORMATIONS ................................... 319
Cation ordering in dolomite ................................ 319
Aragonite → calcite transformation ......................... 321
Observations in sedimentary rocks ....................... 322
Observations of the solid state transformation in the
ТЕМ ..................................................... 326
VARIATIONS IN STACKING ORDER .................................. 328
Periodic basal superstructure in dolomite .................. 328
Stacking disorder and polytypes in rare earth carbonates ... 329
MODULATED STRUCTURES PARALLEL TO r = {1014} .................. 332
Calcian dolomites .......................................... 332
Saddle dolomites ........................................... 338
Calcite .................................................... 343
Carbonatites ............................................... 344
Interpretation ............................................. 348
OTHER SEDIMENTARY CARBONATES .................................. 352
Recent dolomites ........................................... 352
Magnesian calcites ......................................... 352
DEFORMATION ................................................... 354
Deformation mechanisms ..................................... 354
Calcite ................................................. 355
Dolomite ................................................ 356
The effects of twinning .................................... 357
Biaxiality .............................................. 359
Other defects in deformed carbonates ....................... 359
Dislocations ............................................ 359
Stacking faults ......................................... 360
Stylolites - "Pressure solution" ........................ 364
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ............................................... 367
REFERENCES .................................................... 369
APPENDIX
A partial list of some noteworthy papers that have
appeared since the first printing .......................... 395
|