Preface ....................................................... vii
1 Introduction: Hadrons as Systems of Constituent Quarks ....... 1
1.1 Constituent Quarks, Effective Gluons and Hadrons ........ 1
1.2 Naive Quark Model ....................................... 4
1.2.1 Spin-flavour SU(6) symmetry for mesons ........... 5
1.2.2 Low-lying baryons ................................ 8
1.2.3 Spin-flavour SU(6) symmetry for baryons .......... 9
1.3 Estimation of Masses of the Constituent Quarks in the
Quark Model ............................................ 12
1.3.1 Magnetic moments of baryons ..................... 12
1.3.2 Radiative meson decays V → P + γ ................ 13
1.3.3 Empirical mass formulae ......................... 14
1.4 Light Quarks and Highly Excited Hadrons ................ 16
1.4.1 Hadron systematisation .......................... 17
1.4.2 Diquarks ........................................ 18
1.5 Scalar and Tensor Glueballs ............................ 19
1.5.1 Low-lying σ-meson ............................... 22
1.6 High Energies: The Manifestation of the Two- and
Three-Quark Structure of Low-Lying Mesons and
Baryons ................................................ 23
1.6.1 Ratios of total cross sections in nucleoli
Nucleon and pion Nucleon collisions ............. 23
1.6.2 Diffraction cone slopes in elastic nucleoli
Nucleon and pion Nucleon diffraction cross
sections ........................................ 24
1.6.3 Multiplicities of secondary hadrons in e+e-
and hadron-hadron collisions .................... 25
1.6.4 Multiplicities of secondary hadrons in πА and
pA collisions ................................... 26
1.6.5 Momentum fraction carried by quarks at
moderately high energies ........................ 26
1.7 Constituent Quarks, QCD-Quarks, QCD-Gluons and the
Parton Structure of Hadrons ............................ 27
1.7.1 Moderately high energies and constituent
quarks .......................................... 27
1.7.2 Hadron collisions at superhigh energies ......... 28
1.8 Appendix 1.A: Metrics and SU(N) Groups ................. 30
1.8.1 Metrics ......................................... 30
1.8.2 SU(N) groups .................................... 30
2 Systematica of Mesons and Baryons ........................... 37
2.1 Classification of Mesons in the (n, M2) Plane .......... 39
2.1.1 Kaon states ..................................... 43
2.2 Trajectories on (J, M2) Plane .......................... 45
2.2.1 Kaon trajectories on (J, M2) plane .............. 46
2.3 Assignment of Mesons to Nonets ......................... 49
2.4 Baryon Classification on (n, M2) and (J, M2) Planes .... 49
2.5 Assignment of Baryons to Multiplets .................... 51
2.6 Sectors of the 2++ and 0++ Mesons — Observation
of Glueballs ........................................... 54
2.6.1 Tensor mesons ................................... 54
2.6.2 Scalar states ................................... 71
3 Elements of the Scattering Theory ........................... 93
3.1 Scattering in Quantum Mechanics ........................ 93
3.1.1 Schrödinger equation and the wave function
of two scattering particles ..................... 93
3.1.2 Scattering process .............................. 96
3.1.3 Free motion: plane waves and spherical waves .... 96
3.1.4 Scattering process: cross section, partial
wave expansion and phase shifts ................. 97
3.1.5 K-matrix representation, scattering length
approximation and the Breit Wigner resonances ... 99
3.1.6 Scattering with absorption ..................... 101
3.2 Analytical Properties of the Amplitudes ............... 102
3.2.1 Propagator function in quantum mechanics:
the coordinate representation .................. 102
3.2.2 Propagator function in quantum mechanics:
the momentum representation .................... 106
3.2.3 Equation for the scattering amplitude ƒ(k,p) ... 108
3.2.4 Propagators in the description of the two-
particle scattering amplitude .................. 108
3.2.5 Relativistic propagator for a free particle .... 110
3.2.6 Mandelstam plane ............................... 1ll
3.2.7 Dalitz plot .................................... 114
3.3 Dispersion Relation N/D-Method and Bethe Salpeter
Equation .............................................. 114
3.3.1 N/D-method for the one-channel scattering
amplitude of spinless particles ................ 114
3.3.2 N/D-amplitude and K-matrix ..................... 118
3.3.3 Dispersion relation representation and
light-cone variables ........................... 118
3.3.4 Bethe-Salpeter equations in the momentum
representation ................................. 120
3.3.5 Spectral integral equation with separable
kernel in the dispersion relation technique .... 124
3.3.6 Composite system wave function, its
normalisation condition and additive model
for form factors ............................... 126
3.4 The Matrix of Propagators ............................. 130
3.4.1 The mixing of two unstable states .............. 130
3.4.2 The case of many overlapping resonances:
construction of propagator matrices ............ 134
3.4.3 A complete overlap of resonances: the effect
of accumulation of widths by a resonance ....... 135
3.5 К-Matrix Approach ..................................... 136
3.5.1 One-channel amplitude .......................... 136
3.5.2 Multichannel amplitude ......................... 138
3.5.3 The problem of short and large distances ....... 140
3.5.4 Overlapping resonances: broad locking states
and their role in the formation of the
confinement barrier ............................ 142
3.6 Elastic and Quasi-Elastic Meson Meson Reactions ....... 143
3.6.1 Pion exchange reactions ........................ 143
3.6.2 Regge pole propagators ......................... 144
3.7 Appendix 3.A: The ƒ0(980) in Two-Particle and
Production Processes .................................. 147
3.8 Appendix 3.B: K-Matrix Analyses of the (IJPC =
00++)-Wave Partial Amplitude for Reactions ππ →
ππ, КК, ηη, ηη', ππππ ................................. 150
3.9 Appendix 3.C: The K-Matrix Analyses of the (IJP =
1/2 0+)-Wave Partial Amplitude for Reaction πК →
πК .................................................... 160
3.10 Appendix 3.D: The Low-Mass σ-Meson .................... 164
3.10.1 Dispersion relation solution for the ππ-
scattering amplitude below 900 MeV ............. 166
3.11 Appendix 3.E: Cross Sections and Amplitude
Discontinuities ....................................... 170
3.11.1 Exclusive and inclusive cross sections ......... 171
3.11.2 Amplitude discontinuities and unitary
condition ...................................... 173
4 Baryon Baryon and Baryon Antibaryon Systems ................ 179
4.1 Two-Baryon States and Their Scattering Amplitudes ..... 181
4.1.1 Spin-1/2 wave functions ........................ 181
4.1.2 Baryon antibaryon scattering ................... 183
4.1.3 Baryon baryon scattering ....................... 187
4.1.4 Unitarity conditions and K-matrix
representations of the baryon antibaryon and
baryon baryon scattering amplitudes ............ 191
4.1.5 Nucleon-Nucleon scattering amplitude in
the dispersion relation technique with
separable vertices ............................. 197
4.1.6 Comments on the spectral integral equation ..... 204
4.2 Inelastic Processes in NN Collisions: Production of
Mesons ................................................ 208
4.2.1 Reaction pp → two pseudoscalar mesons .......... 209
4.2.2 Reaction pp → ƒ2P3 → Р1Р2P3 ..................... 210
4.3 Inelastic Processes in NN Collisions:
the Production of Δ-Resonances ........................ 212
4.3.1 Spin-3/2 wave functions ........................ 212
4.3.2 Processes NN → NΔ → NNπ Triangle
singularity .................................... 214
4.3.3 The NN → ΔΔ → NNππ process. Box
singularity .................................... 219
4.4 The NN → Nj* + N → NNπ process with j > 3/2 ........... 227
4.5 NAT Scattering Amplitude at Moderately High
Energies the Reggeon Exchanges ........................ 229
4.5.1 Reggeon quark vertices in the two-component
spinor technique ............................... 230
4.5.2 Four-component spinors and reggeon vertices .... 231
4.6 Production of Heavy Particles in the High Energy
Hadron Hadron Collisions: Effects of New Thresholds ... 234
4.6.1 Impact parameter representation of the
scattering amplitude ........................... 234
4.7 Appendix 4.A. Angular Momentum Operators .............. 238
4.7.1 Projection operators and denominators of
the boson propagators .......................... 240
4.7.2 Useful relations for Zαμ1...μn and X(n-1)υ2...υn .... 242
4.8 Appendix 4.B. Vertices for Fermion-Antifermion
States ................................................ 243
4.8.1 Operators for 1LJ states ....................... 244
4.8.2 Operators for 3LJ states with J = L ............ 244
4.8.3 Operators for 3LJ states with L < J and
L > J .......................................... 244
4.9 Appendix 4.C. Spectral Integral Approach with
Separable Vertices: Nucleon-Nucleon Scattering
Amplitude NN → NN, Deuteron Form Factors and
Photodisintegration and the Reaction NN → NΔ .......... 245
4.9.1 The pp → pp and pn → pn scattering
amplitudes ..................................... 246
4.10 Appendix D. NΔ One-Loop Diagrams ...................... 253
4.11 Appendix 4.E. Analysis of the Reactions pp → ππ,
ηη, ηη': Search for ƒj-Mesons ......................... 256
4.12 Appendix 4.F. New Thresholds and the Data for ρ =
Im A/Re A of the UA4 Collaboration at √s = 546 GeV .... 259
4.13 Appendix 4.G. Rescattering Effects in Three-Particle
States: Triangle Diagram Singularities and the
Schmid Theorem ........................................ 264
4.13.1 Visual rules for the determination of
positions of the triangle-diagram
singularities ................................. 266
4.13.2 Calculation of the triangle diagram in terms
of the dispersion relation N/D-method ......... 269
4.13.3 The Breit-Wigner pole and triangle diagrams:
interference effects .......................... 271
4.14 Appendix 4.H. Excited Nucleon States TV(1440) and
N(1710) - Position of Singularities in the
Complex-M Plane ....................................... 274
5 Baryons in the πN and γN Collisions ........................ 279
5.1 Production and Decay of Baryon States ................. 280
5.1.1 The classification of the baryon states ........ 281
5.1.2 The photon and baryon wave functions ........... 281
5.1.3 Pion nucleon and photon-nucleon vertices ....... 284
5.1.4 Photon nucleon vertices ........................ 288
5.2 Single Meson Photoproduction .......................... 292
5.2.1 Photoproduction amplitudes for 1/2-,3/2+;5/2-
states ......................................... 293
5.2.2 Photoproduction amplitudes for 1/2+,3/2-,5/2+,
states ......................................... 294
5.2.3 Relations between the amplitudes in the spin
orbit and helicity representation .............. 294
5.3 The Decay of Baryons into a Pseudoscalar Particle
and a 3/2 State ....................................... 296
5.3.1 Operators for '+' states ....................... 297
5.3.2 Operators for 1/2+, 3/2-, 5/2+, states .......... 297
5.3.3 Operators for the decays J+ → 0- + 3/2+,
J+ → 0+ + 3/2-, J- → 0+ + 3/2+ and J- →
0- + 3/2- ...................................... 298
5.4 Double Pion Photoproduction Amplitudes ................ 298
5.4.1 Amplitudes for baryons states decaying into
a 1/2 state and a pion ......................... 300
5.4.2 Photoproduction amplitudes for baryon states
decaying into a 3/2 state and a pseudoscalar
meson .......................................... 301
5.5 πN and γN Partial Widths of Baryon Resonances ......... 302
5.5.1 πN partial widths of baryon resonances ......... 302
5.5.2 The γN widths and helicity amplitudes .......... 303
5.5.3 Three-body partial widths of the baryon
resonances ..................................... 306
5.5.4 Miniconclusion ................................. 308
5.6 Photoproduction of Baryons Decaying into Nπ and
Nη .................................................... 308
5.6.1 The experimental situation an overview ......... 309
5.6.2 Fits to the data ............................... 311
5.7 Hyperon Photoproduction γp → ΛK+ and γp → ∑K+ .......... 318
5.8 Analyses of γp → π0π0p and γp → π0ηp
Reactions ............................................. 325
5.9 Summary ............................................... 333
5.10 Appendix 5.A. Legendre Polynomials and Convolutions
of Angular Momentum Operators ......................... 333
5.10.1 Some properties of Legendre polynomials ........ 333
5.10.2 Convolutions of angular momentum operators ..... 334
5.11 Appendix 5.B: Cross Sections and Partial Widths for
the Breit Wigner Resonance Amplitudes ................. 335
5.11.1 The Breit Wigner resonance and rescattering
of particles in the resonance state ............ 337
5.11.2 Blatt-Weisskopf form factors ................... 338
5.12 Appendix 5.С Multipoles ............................... 339
6 Multiparticle Production Processes ......................... 343
6.1 Three-Particle Production at Intermediate Energies .... 345
6.1.1 Isobar model ................................... 346
6.1.2 Dispersion integral equation for a three-body
system ......................................... 351
6.1.3 Description of the three-meson production in
the A-matrix approach .......................... 365
6.2 Meson Nucleon Collisions at High Energies:
Peripheral Two-Meson Production in Terms of Reggeon
Exchanges ............................................. 378
6.2.1 Reggeon exchange technique and the K-matrix
analysis of meson spectra in the, waves JPC =
0++, 1--, 2++, 3--, 4++ in high energy
reactions πN → two mesons + N .................. 379
6.2.2 Results of the K-matrix fit of two-meson
systems produced in the peripheral
productions .................................... 389
6.3 Appendix 6.A. Three-meson production PP → πππ,
ππη, πηη .............................................. 396
6.4 Appendix 6.B. Reggeon Exchanges in the Two-Meson
Production Reactions Calculation Routine and Some
Useful Relations ...................................... 399
6.4.1 Reggeised pion exchanges ....................... 400
7 Photon Induced Hadron Production, Meson Form Factors and
Quark Model ................................................ 413
7.1 A System of Two Vector Particles ...................... 415
7.1.1 General structure of spin orbital operators
for the system of two vector mesons ............ 415
7.1.2 Transitions γ*γ* → hadrons ..................... 418
7.1.3 Quark structure of meson production
processes ...................................... 421
7.2 Nilpotent Operators Production of Scalar States ...... 423
7.2.1 Gauge invariance and orthogonality of the
operators ...................................... 423
7.2.2 Transition amplitude γγ* → S when one of the
photons is real ................................ 425
7.3 Reaction e+e- → γ* → γππ .............................. 427
7.3.1 Analytical structure of amplitudes in the
reactions e+e- → γ* → 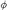 → γ(ππ)S → → γ(ππ)S → 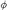 →
γƒ0 and →
γƒ0 and 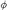 → γ(ππ)S ............................. 427
7.3.2 Decay → γ(ππ)S ............................. 427
7.3.2 Decay 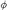 (1020) → γππ: Non-relativistic
quark model calculation of the form factor (1020) → γππ: Non-relativistic
quark model calculation of the form factor
 (1020) → γƒ0bare(700) and the if-matrix
consideration of the transition ƒ0(bare)(700)
→ ππ ........................................... 434
7.3.3 Form factors in the additive quark model and
confinement .................................... 449
7.4 Spectral Integral Technique in the Additive Quark
Model: Transition Amplitudes and Partial Widths of
the Decays (qq)in → γ + V(qq) ......................... 454
7.4.1 Radiative transitions P → γV and S → γV ........ 456
7.4.2 Transitions T(2++) → γV and A(1++) → γV ......... 463
7.5 Determination of the Quark-Antiquark Component of
the Photon Wave Function for u, d, s-Quarks ........... 471
7.5.1 Transition form factors π0, η, η' →
γ*(Q12)γ*(Q22) .................................. 474
7.5.2 e+e--annihilation .............................. 476
7.5.3 Photon wave function ........................... 478
7.5.4 Transitions S → γγ and T → γγ .................. 481
7.6 Nucleon Form Factors .................................. 486
7.6.1 Quark-nucleon vertex ........................... 486
7.6.2 Nucleon form factor - relativistic
description .................................... 490
7.6.3 Nucleon form factors - non-relativistic
calculation .................................... 492
7.7 Appendix 7.A: Pion Charge Form Factor and Pion qq
Wave Function ......................................... 495
7.8 Appendix 7.B: Two-Photon Decay of Scalar and Tensor
Mesons ................................................ 498
7.8.1 Decay of scalar mesons ......................... 498
7.8.2 Tensor-meson decay amplitudes for the
process qq (2++) → γγ .......................... 499
7.9 Appendix 7.C: Comments about Efficiency of QCD Sum
Rules ................................................. 501
8 Spectral Integral Equation ................................. 507
8.1 Basic Standings in the Consideration of Light Meson
Levels in the Framework of the Spectral Integral
Equation .............................................. 508
8.2 Spectral Integral Equation ............................ 511
8.3 Light Quark Mesons .................................... 515
8.3.1 Short-range interactions and confinement ....... 517
8.3.2 Masses and mean radii squared of mesons with
L ≤ 4 .......................................... 519
8.3.3 Trajectories on the (n, M2) planes ............. 523
8.4 Radiative decays ...................................... 524
8.4.1 Wave functions of the quark antiquark states ... 527
8.5 Appendix 8.A: Bottomonium States Found from Spectral
Integral Equation and Radiative Transitions ........... 527
8.5.1 Masses of the bb states ........................ 528
8.5.2 Radiative decays (bb)in, → γ(bb)out ............. 529
8.5.3 The bb component of the photon wave function
and the e+e- → V(bb) and bb-meson → γγ
transitions .................................... 532
8.6 Appendix 8.B: Charmonium States ....................... 535
8.6.1 Radiative transitions (cc)in → γ + (cc)out ...... 536
8.6.2 The cc component of the photon wave function
and two-photon radiative decays ................ 538
8.7 Appendix 8.C: The Fierz Transformation and the
Structure of the t-Channel Exchanges .................. 541
8.8 Appendix 8.D: Spectral Integral Equation for
Composite Systems Built by Spinless Constituents ...... 544
8.8.1 Spectral integral equation for a vertex
function with L = 0 ............................ 544
8.9 Appendix 8.E: Wave Functions in the Sector of the
Light Quarks .......................................... 549
8.10 Appendix 8.F: How Quarks Escape from the Confinement
Trap? ................................................. 558
9 Outlook .................................................... 563
9.1 Quark Structure of Mesons and Baryons ................. 563
9.2 Systematics of the (gq)-Mesons and Baryons ............ 565
9.3 Additive Quark Model, Radiative Decays and Spectral
Integral Equation ..................................... 568
9.4 Resonances and Their Characteristics .................. 570
9.5 Exotic States - Glueballs ............................. 572
9.6 White Remnants of the Confinement Singularities ....... 574
9.7 Quark Escape from Confinement Trap .................... 576
Index ......................................................... 579 (1020) → γƒ0bare(700) and the if-matrix
consideration of the transition ƒ0(bare)(700)
→ ππ ........................................... 434
7.3.3 Form factors in the additive quark model and
confinement .................................... 449
7.4 Spectral Integral Technique in the Additive Quark
Model: Transition Amplitudes and Partial Widths of
the Decays (qq)in → γ + V(qq) ......................... 454
7.4.1 Radiative transitions P → γV and S → γV ........ 456
7.4.2 Transitions T(2++) → γV and A(1++) → γV ......... 463
7.5 Determination of the Quark-Antiquark Component of
the Photon Wave Function for u, d, s-Quarks ........... 471
7.5.1 Transition form factors π0, η, η' →
γ*(Q12)γ*(Q22) .................................. 474
7.5.2 e+e--annihilation .............................. 476
7.5.3 Photon wave function ........................... 478
7.5.4 Transitions S → γγ and T → γγ .................. 481
7.6 Nucleon Form Factors .................................. 486
7.6.1 Quark-nucleon vertex ........................... 486
7.6.2 Nucleon form factor - relativistic
description .................................... 490
7.6.3 Nucleon form factors - non-relativistic
calculation .................................... 492
7.7 Appendix 7.A: Pion Charge Form Factor and Pion qq
Wave Function ......................................... 495
7.8 Appendix 7.B: Two-Photon Decay of Scalar and Tensor
Mesons ................................................ 498
7.8.1 Decay of scalar mesons ......................... 498
7.8.2 Tensor-meson decay amplitudes for the
process qq (2++) → γγ .......................... 499
7.9 Appendix 7.C: Comments about Efficiency of QCD Sum
Rules ................................................. 501
8 Spectral Integral Equation ................................. 507
8.1 Basic Standings in the Consideration of Light Meson
Levels in the Framework of the Spectral Integral
Equation .............................................. 508
8.2 Spectral Integral Equation ............................ 511
8.3 Light Quark Mesons .................................... 515
8.3.1 Short-range interactions and confinement ....... 517
8.3.2 Masses and mean radii squared of mesons with
L ≤ 4 .......................................... 519
8.3.3 Trajectories on the (n, M2) planes ............. 523
8.4 Radiative decays ...................................... 524
8.4.1 Wave functions of the quark antiquark states ... 527
8.5 Appendix 8.A: Bottomonium States Found from Spectral
Integral Equation and Radiative Transitions ........... 527
8.5.1 Masses of the bb states ........................ 528
8.5.2 Radiative decays (bb)in, → γ(bb)out ............. 529
8.5.3 The bb component of the photon wave function
and the e+e- → V(bb) and bb-meson → γγ
transitions .................................... 532
8.6 Appendix 8.B: Charmonium States ....................... 535
8.6.1 Radiative transitions (cc)in → γ + (cc)out ...... 536
8.6.2 The cc component of the photon wave function
and two-photon radiative decays ................ 538
8.7 Appendix 8.C: The Fierz Transformation and the
Structure of the t-Channel Exchanges .................. 541
8.8 Appendix 8.D: Spectral Integral Equation for
Composite Systems Built by Spinless Constituents ...... 544
8.8.1 Spectral integral equation for a vertex
function with L = 0 ............................ 544
8.9 Appendix 8.E: Wave Functions in the Sector of the
Light Quarks .......................................... 549
8.10 Appendix 8.F: How Quarks Escape from the Confinement
Trap? ................................................. 558
9 Outlook .................................................... 563
9.1 Quark Structure of Mesons and Baryons ................. 563
9.2 Systematics of the (gq)-Mesons and Baryons ............ 565
9.3 Additive Quark Model, Radiative Decays and Spectral
Integral Equation ..................................... 568
9.4 Resonances and Their Characteristics .................. 570
9.5 Exotic States - Glueballs ............................. 572
9.6 White Remnants of the Confinement Singularities ....... 574
9.7 Quark Escape from Confinement Trap .................... 576
Index ......................................................... 579
|