Volume II
Preface ......................................................... v
Part III. Analytic Tools
9. Bernoulli Polynomials and the Gamma Function ................ 3
9.1. Bernoulli Numbers and Polynomials ...................... 3
9.1.1. Generating Functions for Bernoulli
Polynomials ..................................... 3
9.1.2. Further Recurrences for Bernoulli
Polynomials .................................... 10
9.1.3. Computing a Single Bernoulli Number ............ 14
9.1.4. Bernoulli Polynomials and Fourier Series ....... 16
9.2. Analytic Applications of Bernoulli Polynomials ........ 19
9.2.1. Asymptotic Expansions .......................... 19
9.2.2. The Euler-MacLaurin Summation Formula .......... 21
9.2.3. The Remainder Term and the Constant Term ....... 25
9.2.4. Euler-MacLaurin and the Laplace Transform ...... 27
9.2.5. Basic Applications of the Euler-MacLaurin
Formula ........................................ 31
9.3. Applications to Numerical Integration ................. 35
9.3.1. Standard Euler-MacLaurin Numerical
Integration .................................... 36
9.3.2. The Basic Tanh-Sinh Numerical Integration
Method ......................................... 37
9.3.3. General Doubly Exponential Numerical
Integration .................................... 39
9.4. χ-Bernoulli Numbers, Polynomials, and Functions ....... 43
9.4.1. χ-Bernoulli Numbers and Polynomials ............ 43
9.4.2. χ-Bernoulli Functions .......................... 46
9.4.3. The χ-Euler-MacLaurin Summation Formula ........ 50
9.5. Arithmetic Properties of Bernoulli Numbers ............ 52
9.5.1. χ-Power Sums ................................... 52
9.5.2. The Generalized Clausen-von Staudt
Congruence ..................................... 61
9.5.3. The Voronoi Congruence ......................... 64
9.5.4. The Kummer Congruences ......................... 67
9.5.5. The Almkvist-Meurman Theorem ................... 70
9.6. The Real and Complex Gamma Functions .................. 71
9.6.1. The Hurwitz Zeta Function ...................... 71
9.6.2. Definition of the Gamma Function ............... 77
9.6.3. Preliminary Results for the Study of Γ(s) ...... 81
9.6.4. Properties of the Gamma Function ............... 84
9.6.5. Specific Properties of the Function ψ(s) ....... 95
9.6.6. Fourier Expansions of ζ(s, x) and log(Γ(x)) ... 100
9.7. Integral Transforms .................................. 103
9.7.1. Generalities on Integral Transforms ........... 104
9.7.2. The Fourier Transform ......................... 104
9.7.3. The Mellin Transform .......................... 107
9.7.4. The Laplace Transform ......................... 108
9.8. Bessel Functions ..................................... 109
9.8.1. Definitions ................................... 109
9.8.2. Integral Representations and Applications ..... 113
9.9. Exercises for Chapter 9 .............................. 118
10. Dirichlet Series and L-Functions .......................... 151
10.1. Arithmetic Functions and Dirichlet Series ........... 151
10.1.1. Operations on Arithmetic Functions .......... 152
10.1.2. Multiplicative Functions .................... 154
10.1.3. Some Classical Arithmetical Functions ....... 155
10.1.4. Numerical Dirichlet Series .................. 160
10.2. The Analytic Theory of L-Series ..................... 162
10.2.1. Simple Approaches to Analytic
Continuation ................................ 163
10.2.2. The Use of the Hurwitz Zeta Function
ζ(s, x) ..................................... 168
10.2.3. The Functional Equation for the Theta
Function .................................... 169
10.2.4. The Functional Equation for Dirichlet
L-Functions ................................. 172
10.2.5. Generalized Poisson Summation Formulas ...... 177
10.2.6. Voronoi's Error Term in the Circle
Problem ..................................... 182
10.3. Special Values of Dirichlet L-Functions ............. 186
10.3.1. Basic Results on Special Values ............. 186
10.3.2. Special Values of L-Functions and Modular
Forms ....................................... 193
10.3.3. The Polya Vinogradov Inequality ............. 198
10.3.4. Bounds and Averages for L(χ, 1) ............. 200
10.3.5. Expansions of ζ(s) Around s = к 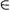 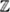 ≤1 ....... 205
10.3.6. Numerical Computation of Euler Products and
Sums ........................................ 208
10.4. Epstein Zeta Functions .............................. 210
10.4.1. The Nonholomorphic Eisenstein Series
G(τ, s) ..................................... 211
10.4.2. The Kronecker Limit Formula ................. 213
10.5. Dirichlet Series Linked to Number Fields ............ 216
10.5.1. The Dedekind Zeta Function ζK(s) ............ 216
10.5.2. The Dedekind Zeta Function of Quadratic
Fields ...................................... 219
10.5.3. Applications of the Kronecker Limit
Formula ..................................... 223
10.5.4. The Dedekind Zeta Function of Cyclotomic
Fields ...................................... 230
10.5.5. The Nonvanishing of L(χ, 1) ................. 235
10.5.6. Application to Primes in Arithmetic
Progression ................................. 237
10.5.7. Conjectures on Dirichlet L-Functions ........ 238
10.6. Science Fiction on L-Functions ...................... 239
10.6.1. Local L-Functions ........................... 239
10.6.2. Global L-Functions .......................... 241
10.7. The Prime Number Theorem ............................ 245
10.7.1. Estimates for ζ(s) .......................... 246
10.7.2. Newman's Proof .............................. 250
10.7.3. Iwaniec's Proof ............................. 254
10.8. Exercises for Chapter 10 ............................ 258
11. p-adic Gamma and L-Functions .............................. 275
11.1. Generalities on p-adic Functions .................... 275
11.1.1. Methods for Constructing p-adic Functions ... 275
11.1.2. A Brief Study of Volkenborn Integrals ....... 276
11.2. The p-adic Hurwitz Zeta Functions ................... 280
11.2.1. Teichmtiller Extensions and Characters
on ≤1 ....... 205
10.3.6. Numerical Computation of Euler Products and
Sums ........................................ 208
10.4. Epstein Zeta Functions .............................. 210
10.4.1. The Nonholomorphic Eisenstein Series
G(τ, s) ..................................... 211
10.4.2. The Kronecker Limit Formula ................. 213
10.5. Dirichlet Series Linked to Number Fields ............ 216
10.5.1. The Dedekind Zeta Function ζK(s) ............ 216
10.5.2. The Dedekind Zeta Function of Quadratic
Fields ...................................... 219
10.5.3. Applications of the Kronecker Limit
Formula ..................................... 223
10.5.4. The Dedekind Zeta Function of Cyclotomic
Fields ...................................... 230
10.5.5. The Nonvanishing of L(χ, 1) ................. 235
10.5.6. Application to Primes in Arithmetic
Progression ................................. 237
10.5.7. Conjectures on Dirichlet L-Functions ........ 238
10.6. Science Fiction on L-Functions ...................... 239
10.6.1. Local L-Functions ........................... 239
10.6.2. Global L-Functions .......................... 241
10.7. The Prime Number Theorem ............................ 245
10.7.1. Estimates for ζ(s) .......................... 246
10.7.2. Newman's Proof .............................. 250
10.7.3. Iwaniec's Proof ............................. 254
10.8. Exercises for Chapter 10 ............................ 258
11. p-adic Gamma and L-Functions .............................. 275
11.1. Generalities on p-adic Functions .................... 275
11.1.1. Methods for Constructing p-adic Functions ... 275
11.1.2. A Brief Study of Volkenborn Integrals ....... 276
11.2. The p-adic Hurwitz Zeta Functions ................... 280
11.2.1. Teichmtiller Extensions and Characters
on 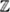 p ....................................... 280
11.2.2. The p-adic Hurwitz Zeta Function
for x p ....................................... 280
11.2.2. The p-adic Hurwitz Zeta Function
for x 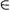 C C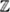 P ................................ 281
11.2.3. The Function ζp(s, x) Around s = 1 .......... 288
11.2.4. The p-adic Hurwitz Zeta Function
for x P ................................ 281
11.2.3. The Function ζp(s, x) Around s = 1 .......... 288
11.2.4. The p-adic Hurwitz Zeta Function
for x 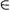 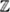 p .................................. 290
11.3. p-adic L-Functions .................................. 300
11.3.1. Dirichlet Characters in the p-adic
Context ..................................... 300
11.3.2. Definition and Basic Properties of p-adic
L-Functions ................................. 301
11.3.3. p-adic L-Functions at Positive Integers ..... 305
11.3.4. χ-Power Sums Involving p-adic Logarithms .... 310
11.3.5. The Function Lp(χ, s) Around s = 1 .......... 317
11.4 Applications of p-adic L-Functions .................. 319
11.4.1. Integrality and Parity of L-Function
Values ...................................... 319
11.4.2. Bernoulli Numbers and Regular Primes ........ 324
11.4.3. Strengthening of the Almkvist-Meurman
Theorem ..................................... 326
11.5. p-adic Log Gamma Functions .......................... 329
11.5.1. Diamond's p-adic Log Gamma Function ......... 330
11.5.2. Morita's p-adic Log Gamma Function .......... 336
11.5.3. Computation of some p-adic Logarithms ....... 346
11.5.4. Computation of Limits of some Logarithmic
Sums ........................................ 356
11.5.5. Explicit Formulas for ψр(r/m) and
ψр(χ,r/m) ................................... 359
11.5.6. Application to the Value of Lp(χ, 1) ........ 361
11.6. Morita's p-adic Gamma Function ...................... 364
11.6.1. Introduction ................................ 364
11.6.2 Definitions and Basic Results ................ 365
11.6.3. Main Properties of the p-adic Gamma
Function .................................... 369
11.6.4. Mahler-Dwork Expansions Linked to Гр(x) ..... 375
11.6.5. Power Series Expansions Linked to Гр(x) ..... 378
11.6.6. The Jacobstahl-Kazandzidis Congruence ....... 380
11.7. The Gross-Koblitz Formula and Applications .......... 383
11.7.1. Statement and Proof of the Gross-Koblitz
Formula ..................................... 383
11.7.2. Application to L'p(χ, 0) .................... 389
11.7.3. Application to trie Stickelberger
Congruence .................................. 390
11.7.4. Application to the Hasse-Davenport Product
Relation .................................... 392
11.8. Exercises for Chapter 11 ............................ 395
Part IV. Modern Tools
12. Applications of Linear Forms in Logarithms .............. . 411
12.1. Introduction ........................................ 411
12.1.1. Lower Bounds ................................ 411
12.1.2. Applications to Diophantine Equations and
Problems .................................... 413
12.1.3. A List of Applications ...................... 414
12.2. A Lower Bound for |2m - 3n| ......................... 415
12.3. Lower Bounds for the Trace of αn .................... 418
12.4. Pure Powers in Binary Recurrent Sequences ........... 420
12.5. Greatest Prime Factors of Terms of Some Recurrent
Sequences ........................................... 421
12.6. Greatest Prime Factors of Values of Integer
Polynomials ......................................... 422
12.7. The Diophantine Equation axn - byn = с .............. 423
12.8. Simultaneous Pell Equations ......................... 424
12.8.1. General Strategy ............................ 424
12.8.2. An Example in Detail ........................ 425
12.8.3. A General Algorithm ......................... 426
12.9. Catalan's Equation .................................. 428
12.10. Thue Equations ..................................... 430
12.10.1. The Main Theorem ........................... 430
12.10.2. Algorithmic Aspects ........................ 432
12.11. Other Classical Diophantine Equations .............. 436
12.12. A Few Words on the Non-Archimedean Case ............ 439
13. Rational Points on Higher-Genus Curves .................... 441
13.1. Introduction ........................................ 441
13.2. The Jacobian ........................................ 442
13.2.1. Functions on Curves ......................... 443
13.2.2. Divisors .................................... 444
13.2.3. Rational Divisors ........................... 445
13.2.4. The Group Law: Cantor's Algorithm ........... 446
13.2.5. The Group Law: The Geometric Point of
View ........................................ 448
13.3. Rational Points on Hyperelliptic Curves ............. 449
13.3.1. The Method of Dem'yanenko-Manin ............. 449
13.3.2. The Method of Chabauty-Coleman .............. 452
13.3.3. Explicit Chabauty According to Flynn ........ 453
13.3.4. When Chabauty Fails ......................... 455
13.3.5. Elliptic Curve Chabauty ..................... 456
13.3.6. A Complete Example .......................... 459
14. The Super-Fermat Equation ................................. 463
14.1. Preliminary Reductions .............................. 463
14.2. The Dihedral Cases (2,2,r) .......................... 465
14.2.1. The Equation x2 - y2 = zr .................... 465
14.2.2. The Equation x2 + y2 = zr .................... 466
14.2.3. The Equations x2 + 3y2 = z3 and
x2 + 3y2 = 4z3 ............................... 466
14.3. The Tctrahcdral Case (2,3,3) ........................ 467
14.3.1. The Equation x3 + y3 = z2 ................... 467
14.3.2. The Equation x3 + y3 = 2z2 .................. 470
14.3.3. The Equation x3 - 2y3 = z2 .................. 472
14.4. The Octahedral Case (2,3,4) ......................... 473
14.4.1. The Equation x2 - y4 = z3 ................... 473
14.4.2. The Equation x2 + y4 = z3 ................... 475
14.5. Invariants, Covariants, and Dessins d'Enfants ....... 477
14.5.1. Dessins d'Enfants, Klein Forms, and
Covariants .................................. 478
14.5.2. The Icosahedral Case (2,3,5) .............. 479
14.6. The Parabolic and Hyperbolic Cases .................. 481
14.6.1. The Parabolic Case .......................... 481
14.6.2. General Results in the Hyperbolic Case ...... 482
14.6.3. The Equations x4 ± y4 = z3 .................. 484
14.6.4. The Equation x4 + y4 = z5 ................... 485
14.6.5. The Equation x6 - y4 = z2 ................... 486
14.6.6. The Equation x4 - y6 = z2 ................... 487
14.6.7. The Equation x6 + y4 = z2 ................... 488
14.6.8. Further Results ............................. 489
14.7. Applications of Mason's Theorem ..................... 490
14.7.1. Mason's Theorem ............................. 491
14.7.2. Applications ................................ 492
14.8. Exercises for Chapter 14 ............................ 493
15. The Modular Approach to Diophantine Equations ............. 495
15.1. Newforms ............................................ 495
15.1.1. Introduction and Necessary Software Tools ... 495
15.1.2. Newforms .................................... 496
15.1.3. Rational Newforms and Elliptic Curves ....... 497
15.2. Ribet's Level-Lowering Theorem ...................... 498
15.2.1. Definition of "Arises From" ................. 498
15.2.2. Ribet's Level-Lowering Theorem .............. 499
15.2.3. Absence of Isogenies ........................ 501
15.2.4. How to use Ribet's Theorem .................. 503
15.3. Format's Last Theorem and Similar Equations ......... 503
15.3.1. A Generalization of FLT ..................... 504
15.3.2. E Arises from a Curve with Complex
Multiplication .............................. 505
15.3.3. End of the Proof of Theorem 15.3.1 .......... 506
15.3.4. The Equation x2 = yp + 2rzp for p ≥ 7 and
r ≥ 2 ....................................... 507
15.3.5. The Equation x2 = yp + zp for p ≥ 7 ......... 509
15.4. An Occasional Bound for the Exponent ................ 509
15.5. An Example of Serre-Mazur-Kraus ..................... 511
15.6. The Method of Kraus ................................. 514
15.7. "Predicting Exponents of Constants" ................. 517
15.7.1. The Diophantine Equation x2 - 2 = yp ........ 517
15.7.2. Application to the SMK Equation ............. 521
15.8. Recipes for Some Ternary Diophantine Equations ...... 522
15.8.1. Recipes for Signature (p,p,p) ............... 523
15.8.2. Recipes for Signature (p,p,2) ............... 524
15.8.3. Recipes for Signature (p,p,3) ............... 526
16. Catalan's Equation ........................................ 529
16.1. Mihailescu's First Two Theorems ..................... 529
16.1.1. The First Theorem: Double Wieferich Pairs ... 530
16.1.2. The Equation (xp - 1)/(x - 1) = pyq ......... 532
16.1.3. Mihailescu's Second Theorem:
p |h‾q and q| h‾p ........................... 536
16.2. The + and — Subspaces and the Group S ............... 537
16.2.1. The + and — Subspaces ....................... 538
16.2.2. The Group S ................................. 540
16.3. Mihailescu's Third Theorem: p < 4q2 and q < 4p2 ..... 542
16.4. Mihailescu's Fourth Theorem: p ≡ 1 (mod q) or
q ≡ 1 (mod p) ....................................... 547
16.4.1. Preliminaries on Commutative Algebra ........ 547
16.4.2. Preliminaries on the Plus Part .............. 549
16.4.3. Cyclotomic Units and Thaine's Theorem ....... 552
16.4.4. Preliminaries on Power Series ............... 554
16.4.5. Proof of Mihailescu's Fourth Theorem ........ 557
16.4.6. Conclusion: Proof of Catalan's Conjecture ... 560
Bibliography .................................................. 561
Index of Notation ............................................. 571
Index of Names ................................................ 579
General Index ................................................. 585 p .................................. 290
11.3. p-adic L-Functions .................................. 300
11.3.1. Dirichlet Characters in the p-adic
Context ..................................... 300
11.3.2. Definition and Basic Properties of p-adic
L-Functions ................................. 301
11.3.3. p-adic L-Functions at Positive Integers ..... 305
11.3.4. χ-Power Sums Involving p-adic Logarithms .... 310
11.3.5. The Function Lp(χ, s) Around s = 1 .......... 317
11.4 Applications of p-adic L-Functions .................. 319
11.4.1. Integrality and Parity of L-Function
Values ...................................... 319
11.4.2. Bernoulli Numbers and Regular Primes ........ 324
11.4.3. Strengthening of the Almkvist-Meurman
Theorem ..................................... 326
11.5. p-adic Log Gamma Functions .......................... 329
11.5.1. Diamond's p-adic Log Gamma Function ......... 330
11.5.2. Morita's p-adic Log Gamma Function .......... 336
11.5.3. Computation of some p-adic Logarithms ....... 346
11.5.4. Computation of Limits of some Logarithmic
Sums ........................................ 356
11.5.5. Explicit Formulas for ψр(r/m) and
ψр(χ,r/m) ................................... 359
11.5.6. Application to the Value of Lp(χ, 1) ........ 361
11.6. Morita's p-adic Gamma Function ...................... 364
11.6.1. Introduction ................................ 364
11.6.2 Definitions and Basic Results ................ 365
11.6.3. Main Properties of the p-adic Gamma
Function .................................... 369
11.6.4. Mahler-Dwork Expansions Linked to Гр(x) ..... 375
11.6.5. Power Series Expansions Linked to Гр(x) ..... 378
11.6.6. The Jacobstahl-Kazandzidis Congruence ....... 380
11.7. The Gross-Koblitz Formula and Applications .......... 383
11.7.1. Statement and Proof of the Gross-Koblitz
Formula ..................................... 383
11.7.2. Application to L'p(χ, 0) .................... 389
11.7.3. Application to trie Stickelberger
Congruence .................................. 390
11.7.4. Application to the Hasse-Davenport Product
Relation .................................... 392
11.8. Exercises for Chapter 11 ............................ 395
Part IV. Modern Tools
12. Applications of Linear Forms in Logarithms .............. . 411
12.1. Introduction ........................................ 411
12.1.1. Lower Bounds ................................ 411
12.1.2. Applications to Diophantine Equations and
Problems .................................... 413
12.1.3. A List of Applications ...................... 414
12.2. A Lower Bound for |2m - 3n| ......................... 415
12.3. Lower Bounds for the Trace of αn .................... 418
12.4. Pure Powers in Binary Recurrent Sequences ........... 420
12.5. Greatest Prime Factors of Terms of Some Recurrent
Sequences ........................................... 421
12.6. Greatest Prime Factors of Values of Integer
Polynomials ......................................... 422
12.7. The Diophantine Equation axn - byn = с .............. 423
12.8. Simultaneous Pell Equations ......................... 424
12.8.1. General Strategy ............................ 424
12.8.2. An Example in Detail ........................ 425
12.8.3. A General Algorithm ......................... 426
12.9. Catalan's Equation .................................. 428
12.10. Thue Equations ..................................... 430
12.10.1. The Main Theorem ........................... 430
12.10.2. Algorithmic Aspects ........................ 432
12.11. Other Classical Diophantine Equations .............. 436
12.12. A Few Words on the Non-Archimedean Case ............ 439
13. Rational Points on Higher-Genus Curves .................... 441
13.1. Introduction ........................................ 441
13.2. The Jacobian ........................................ 442
13.2.1. Functions on Curves ......................... 443
13.2.2. Divisors .................................... 444
13.2.3. Rational Divisors ........................... 445
13.2.4. The Group Law: Cantor's Algorithm ........... 446
13.2.5. The Group Law: The Geometric Point of
View ........................................ 448
13.3. Rational Points on Hyperelliptic Curves ............. 449
13.3.1. The Method of Dem'yanenko-Manin ............. 449
13.3.2. The Method of Chabauty-Coleman .............. 452
13.3.3. Explicit Chabauty According to Flynn ........ 453
13.3.4. When Chabauty Fails ......................... 455
13.3.5. Elliptic Curve Chabauty ..................... 456
13.3.6. A Complete Example .......................... 459
14. The Super-Fermat Equation ................................. 463
14.1. Preliminary Reductions .............................. 463
14.2. The Dihedral Cases (2,2,r) .......................... 465
14.2.1. The Equation x2 - y2 = zr .................... 465
14.2.2. The Equation x2 + y2 = zr .................... 466
14.2.3. The Equations x2 + 3y2 = z3 and
x2 + 3y2 = 4z3 ............................... 466
14.3. The Tctrahcdral Case (2,3,3) ........................ 467
14.3.1. The Equation x3 + y3 = z2 ................... 467
14.3.2. The Equation x3 + y3 = 2z2 .................. 470
14.3.3. The Equation x3 - 2y3 = z2 .................. 472
14.4. The Octahedral Case (2,3,4) ......................... 473
14.4.1. The Equation x2 - y4 = z3 ................... 473
14.4.2. The Equation x2 + y4 = z3 ................... 475
14.5. Invariants, Covariants, and Dessins d'Enfants ....... 477
14.5.1. Dessins d'Enfants, Klein Forms, and
Covariants .................................. 478
14.5.2. The Icosahedral Case (2,3,5) .............. 479
14.6. The Parabolic and Hyperbolic Cases .................. 481
14.6.1. The Parabolic Case .......................... 481
14.6.2. General Results in the Hyperbolic Case ...... 482
14.6.3. The Equations x4 ± y4 = z3 .................. 484
14.6.4. The Equation x4 + y4 = z5 ................... 485
14.6.5. The Equation x6 - y4 = z2 ................... 486
14.6.6. The Equation x4 - y6 = z2 ................... 487
14.6.7. The Equation x6 + y4 = z2 ................... 488
14.6.8. Further Results ............................. 489
14.7. Applications of Mason's Theorem ..................... 490
14.7.1. Mason's Theorem ............................. 491
14.7.2. Applications ................................ 492
14.8. Exercises for Chapter 14 ............................ 493
15. The Modular Approach to Diophantine Equations ............. 495
15.1. Newforms ............................................ 495
15.1.1. Introduction and Necessary Software Tools ... 495
15.1.2. Newforms .................................... 496
15.1.3. Rational Newforms and Elliptic Curves ....... 497
15.2. Ribet's Level-Lowering Theorem ...................... 498
15.2.1. Definition of "Arises From" ................. 498
15.2.2. Ribet's Level-Lowering Theorem .............. 499
15.2.3. Absence of Isogenies ........................ 501
15.2.4. How to use Ribet's Theorem .................. 503
15.3. Format's Last Theorem and Similar Equations ......... 503
15.3.1. A Generalization of FLT ..................... 504
15.3.2. E Arises from a Curve with Complex
Multiplication .............................. 505
15.3.3. End of the Proof of Theorem 15.3.1 .......... 506
15.3.4. The Equation x2 = yp + 2rzp for p ≥ 7 and
r ≥ 2 ....................................... 507
15.3.5. The Equation x2 = yp + zp for p ≥ 7 ......... 509
15.4. An Occasional Bound for the Exponent ................ 509
15.5. An Example of Serre-Mazur-Kraus ..................... 511
15.6. The Method of Kraus ................................. 514
15.7. "Predicting Exponents of Constants" ................. 517
15.7.1. The Diophantine Equation x2 - 2 = yp ........ 517
15.7.2. Application to the SMK Equation ............. 521
15.8. Recipes for Some Ternary Diophantine Equations ...... 522
15.8.1. Recipes for Signature (p,p,p) ............... 523
15.8.2. Recipes for Signature (p,p,2) ............... 524
15.8.3. Recipes for Signature (p,p,3) ............... 526
16. Catalan's Equation ........................................ 529
16.1. Mihailescu's First Two Theorems ..................... 529
16.1.1. The First Theorem: Double Wieferich Pairs ... 530
16.1.2. The Equation (xp - 1)/(x - 1) = pyq ......... 532
16.1.3. Mihailescu's Second Theorem:
p |h‾q and q| h‾p ........................... 536
16.2. The + and — Subspaces and the Group S ............... 537
16.2.1. The + and — Subspaces ....................... 538
16.2.2. The Group S ................................. 540
16.3. Mihailescu's Third Theorem: p < 4q2 and q < 4p2 ..... 542
16.4. Mihailescu's Fourth Theorem: p ≡ 1 (mod q) or
q ≡ 1 (mod p) ....................................... 547
16.4.1. Preliminaries on Commutative Algebra ........ 547
16.4.2. Preliminaries on the Plus Part .............. 549
16.4.3. Cyclotomic Units and Thaine's Theorem ....... 552
16.4.4. Preliminaries on Power Series ............... 554
16.4.5. Proof of Mihailescu's Fourth Theorem ........ 557
16.4.6. Conclusion: Proof of Catalan's Conjecture ... 560
Bibliography .................................................. 561
Index of Notation ............................................. 571
Index of Names ................................................ 579
General Index ................................................. 585
|