|
 | Spectral methods. Evolution to complex geometries and applications to fluid dynamics / ed. by Canuto C.G., Hussaini M.Y., Quarteroni A., Zang T.A. - Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag GmbH., 2007. - 596 p. - (Scientific computation). - ISSN 1434-8322; ISBN 978-540-30727-3
|
1. Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics .............................. 1
1.1. Introduction .......................................... 1
1.2. Fluid Dynamics Background ............................. 1
1.2.1. Phases of Matter .............................. 2
1.2.2. Thermodynamic Relationships ................... 3
1.2.3. Historical Perspective ........................ 6
1.3. Compressible Fluid Dynamics Equations ................. 7
1.3.1. Compressible Navier-Stokes Equations .......... 8
1.3.2. Nondimensionalization ........................ 12
1.3.3. Navier-Stokes Equations with Turbulence
Models ....................................... 13
1.3.4. Compressible Euler Equations ................. 17
1.3.5. Compressible Potential Equation .............. 17
1.3.6. Compressible Boundary-Layer Equations ........ 19
1.3.7. Compressible Stokes Limit .................... 20
1.3.8. Low Mach Number Compressible Limit ........... 21
1.4. Incompressible Fluid Dynamics Equations .............. 21
1.4.1. Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations ....... 21
1.4.2. Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations
with Turbulence Models ....................... 22
1.4.3. Vorticity-Streamfunction Equations ........... 25
1.4.4. Vorticity-Velocity Equations ................. 26
1.4.5. Incompressible Boundary-Layer Equations ...... 27
1.5. Linear Stability of Parallel Flows ................... 27
1.5.1. Incompressible Linear Stability .............. 29
1.5.2. Compressible Linear Stability ................ 31
1.6. Stability Equations for Nonparallel Flows ............ 36
2. Single-Domain Methods for Stability Analysis ............... 39
2.1. Introduction ......................................... 39
2.2. Boundary-Layer Flows ................................. 41
2.2.1. Incompressible Boundary-Layer Flows .......... 41
2.2.2. Compressible Boundary-Layer Flows ............ 48
2.3. Linear Stability of Incompressible Parallel Flows .... 52
2.3.1. Spectral Approximations for Plane
Poiseuille Flow .............................. 52
2.3.2. Numerical Examples for Plane Poiseuille
Flow ......................................... 57
2.3.3. Some Other Incompressible Linear Stability
Problems ..................................... 61
2.4. Linear Stability of Compressible Parallel Flows ...... 64
2.5. Nonparallel Linear Stability ......................... 69
2.5.1. Linear Parabolized Stability Equations ....... 69
2.5.2. Two-Dimensional Global Stability Analysis .... 71
2.6. Transient Growth Analysis ............................ 72
2.7. Nonlinear Stability .................................. 75
2.7.1. Quasi-Steady Finite-Amplitude Solutions ...... 75
2.7.2. Secondary Instability Theory ................. 77
2.7.3. Nonlinear Parabolized Stability Equations .... 81
3. Single-Domain Methods for Incompressible Flows ............. 83
3.1. Introduction ......................................... 83
3.2. Conservation Properties and Time-Discretization ...... 86
3.2.1. Conservation Properties ...................... 86
The Rotation Form ............................ 88
The Skew-Symmetric Form ...................... 90
Convection and Divergence Forms .............. 92
3.2.2. General Guidelines for Time-Discretization ... 92
3.2.3. Coupled Methods .............................. 93
Fully Implicit Schemes ....................... 93
Semi-Implicit Schemes ........................ 93
3.2.4. Splitting Methods ............................ 95
3.2.5. Other Integration Methods .................... 96
Operator Integration Factors ................. 96
Characteristics Methods ...................... 97
3.3. Homogeneous Flows .................................... 98
3.3.1. Fourier Galerkin Approximation for
Isotropic Turbulence ......................... 98
3.3.2. De-aliasing Using Transform Methods .......... 99
3.3.3. Pseudospectral and Collocation Methods ...... 103
3.3.4. Rogallo Transformation for Homogeneous
Turbulence .................................. 106
3.3.5. Large-Eddy Simulation of Isotropic
Turbulence .................................. 108
3.3.6. The Taylor-Green Vortex Example:
Stability, Accuracy and Aliasing ............ 110
3.4. Flows with One Inhomogeneous Direction .............. 121
3.4.1. Coupled Methods ............................. 123
Kleiser-Schumann Algorithm .................. 124
Normal Velocity-Normal Vorticity
Algorithms .................................. 127
3.4.2. Galerkin Methods Using Divergence-Free
Bases ....................................... 131
3.4.3. Splitting Methods ........................... 133
Chebyshev Staggered Grid .................... 133
Zang-Hussaini Algorithm ..................... 135
3.4.4. Other Confined Flows ........................ 138
3.4.5. Unbounded Flows ............................. 140
Flat-Plate Boundary-Layer Flows ............. 140
Free-Shear-Layer Flows ...................... 142
3.4.6. A Numerical Example: Accuracy ............... 144
3.5. Flows with Multiple Inhomogeneous Directions ........ 147
3.5.1. The Choice of Spatial Discretization in a
Cavity ...................................... 149
3.5.2. The Choice of Spatial Discretization on a
Reference Domain ............................ 157
3.6. Outflow Boundary Conditions ......................... 159
3.6.1. Fringe Regions .............................. 159
3.6.2. Buffer Domains .............................. 161
3.7. Analysis of Spectral Methods for Incompressible
Flows ............................................... 162
3.7.1. Compatibility Conditions Between Velocity
and Pressure ................................ 165
3.7.2. Direct Discretization of the Continuity
Equation: The Inf-sup Condition ............. 168
General Theory .............................. 169
3.7.3. Specific Applications ....................... 172
Numerical Results ........................... 177
Extensions .................................. 178
3.7.4. The Inf-sup Condition and the Pressure
Operator .................................... 179
3.7.5. Discretizations of the Continuity Equation
by an Influence-Matrix Technique: The
Kleiser-Schumann Method ..................... 183
4. Single-Domain Methods for Compressible Flows .............. 187
4.1. Introduction ........................................ 187
4.2. Boundary Treatment for Hyperbolic Systems ........... 187
4.2.1. Characteristic Compatibility Conditions ..... 188
An Example of Unstable Treatment ............ 188
The Characteristic Compatibility Method
(CCM) ....................................... 189
CCM for a General ID System ................. 192
CCM for the Collocation Method .............. 193
CCM for a General Multidimensional
System ...................................... 195
References and Outlook ...................... 196
4.2.2. Boundary Treatment for Linear Systems in
Weak Formulations ........................... 197
4.2.3. Spectral Accuracy and Conservation .......... 199
4.2.4. Analysis of Spectral Methods for Symmetric
Hyperbolic Systems .......................... 200
4.3. Boundary Treatment for the Euler Equations .......... 203
4.4. High-Frequency Control .............................. 208
4.5. Homogeneous Turbulence .............................. 211
4.5.1. Algorithmic Considerations .................. 211
4.5.2. Representative Applications ................. 214
4.6. Smooth, Inhomogeneous Flows ......................... 218
4.6.1. Euler Equations ............................. 218
4.6.2. Navier-Stokes Equations ..................... 221
4.6.3. Numerical Example ........................... 224
4.7. Shock Fitting ....................................... 226
4.8. Shock Capturing ..................................... 233
5. Multidomain Discretizations ............................... 237
5.1. Introduction ........................................ 237
5.2. The Spectral Element Method (SEM) in ID ............. 239
5.2.1. SEM Formulation ............................. 239
5.2.2. Construction of SEM Basis Functions ......... 241
5.2.3. SEM-NI and its Collocation Interpretation ... 243
5.3. SEM for Multidimensional Problems ................... 245
5.3.1. Construction of SEM Function Spaces ......... 245
5.3.2. Construction of SEM Basis Functions ......... 247
5.3.3. SEM and SEM-NI Formulations ................. 250
5.3.4. Algebraic Aspects of SEM and SEM-NI ......... 252
5.3.5. Finite-Element Preconditioning of SEM-NI
Matrices .................................... 253
5.4. Analysis of SEM and SEM-NI Approximations ........... 257
5.4.1. One-Dimensional Analysis .................... 257
A Priori Error Analysis for SEM ............. 258
A Priori Analysis for SEM-NI ................ 260
A Posteriori Error Analysis ................. 261
5.4.2. Multidimensional Analysis ................... 263
A Priori Error Analysis ..................... 264
A Posteriori Error Analysis ................. 265
5.4.3. Some Proofs ................................. 268
5.5. Some Numerical Results for the SEM-NI
Approximations ...................................... 273
5.5.1. Error Decay vs. N and h ..................... 273
5.5.2. Eigenfunction Approximation ................. 275
5.6. SEM for Stokes and Navier-Stokes Equations .......... 278
5.6.1. SEM and SEM-NI Formulations ................. 279
5.6.2. Stability and Convergence Analysis .......... 283
Proof of the Global Inf-sup Condition ....... 285
5.6.3. Numerical Results ........................... 286
5.7. The Mortar Element Method (MEM) ..................... 289
5.7.1. Formulation of MEM .......................... 290
5.7.2. Algebraic Aspects of MEM .................... 294
5.7.3. Analysis of MEM ............................. 296
5.7.4. Other Applications .......................... 299
5.8. The Spectral Discontinuous Galerkin Method (SDGM)
in ID ............................................... 300
5.8.1. Linear Advection Problems in ID ............. 301
5.8.2. Linear Hyperbolic Systems in ID ............. 303
5.8.3. Time-Dependent Problems ..................... 308
5.8.4 Nonlinear Conservation Laws in ID ............. 313
5.9. SDGM for Multidimensional Problems .................. 316
5.9.1. Multidimensional Formulation ................ 317
Linear Problems ............................. 317
Nonlinear Conservation Laws ................. 319
5.9.2. The Mortar Technique for Geometrical
Nonconformities ............................. 321
5.10. SDGM for Diffusion Equations ........................ 323
5.11. Analysis of SDGM .................................... 326
5.12. SDGM for Euler and Navier-Stokes Equations .......... 332
Approximate Numerical Fluxes ........................ 332
Time-Discretizations ................................ 333
Numerical Examples .................................. 334
Shock Tracking ...................................... 337
5.13. The Patching Method ................................. 339
5.13.1. Formulation of Patching Methods ............. 339
5.13.2. Comparison of Patching and SEM-NI ........... 343
5.13.3. Collocation Methods for the Euler
Equations ................................... 345
Collocation Using a Nonstaggered Grid ....... 346
Collocation Using a Staggered Grid .......... 348
Multidomain Shock Fitting ................... 350
5.14. 3D Applications in Complex Geometries ............... 352
5.14.1. The Spectral Element Method: Application
to Incompressible Flow ...................... 352
5.14.2. The Spectral Discontinuous Galerkin
Method: Application to Compressible Flow .... 353
5.14.3. The Spectral Element Method: Application
to Thermoelasticity ......................... 354
5.14.4. The Spectral Element Method: Structural
Dynamics Analysis of the Roman Colosseum .... 356
6. Multidomain Solution Strategies ........................... 359
6.1. Introduction ........................................ 359
6.2. On Domain Decomposition Preconditioners ............. 359
6.3. (Overlapping) Schwarz Alternating Methods ........... 364
6.3.1. Algebraic Form of Schwarz Methods for
Finite-Element Discretization ............... 367
6.3.2. The Schwarz Method as an Algebraic
Preconditioner .............................. 370
6.3.3. Additive Schwarz Preconditioners for
High-Order Methods .......................... 373
6.3.4. FEM-SEM Spectral Equivalence ................ 380
6.3.5. Analysis of Schwarz Methods ................. 381
6.3.6. A General Theoretical Framework for the
Analysis of DD Iterations ................... 383
6.4. Schur Complement Iterative Methods .................. 385
6.4.1. The Steklov-Poincare Interface Problem ...... 385
6.4.2. Properties of the Steklov-Poincare
Operator .................................... 387
6.4.3. The Schur Complement Matrix ................. 387
6.4.4. DD Preconditioners for the Schur
Complement Matrix............................ 393
6.4.5. Preconditioners for the Stiffness Matrix
Derived from Preconditioners for the Schur
Complement Matrix ........................... 398
6.5. Solution Algorithms for Patching Collocation
Methods ............................................. 402
7. Incompressible Flows in Complex Domains ................... 407
7.1. Introduction ........................................ 407
7.2. High-Order Fractional-Step Methods .................. 409
7.3. Solution of Generalized Stokes System ............... 415
7.3.1. Preconditioners for the Generalized Stokes
Matrix 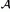 .................................... 416
7.3.2. Conditioning and Preconditioning for the
Pressure Schur Complement Matrix ............ 419
7.3.3. Domain Decomposition Preconditioners for
the Stokes and Navier-Stokes Equations ...... 421
7.4. Algebraic Factorization Methods ..................... 425
7.4.1. Chorin-Temam and Yosida Algebraic
Factorization Methods ....................... 425
7.4.2. Numerical Results for Yosida Schemes ........ 428
7.4.3. Preconditioners for the Approximate
Pressure Schur Complement ................... 430
8. Spectral Methods Primer ................................... 435
8.1. The Fourier System .................................. 435
The Fourier Series .................................. 436
Truncation and Projection ........................... 436
Decay of the Fourier Coefficients ................... 437
Discrete Fourier Expansion and Interpolation ........ 438
Aliasing ............................................ 440
Differentiation ..................................... 441
Gibbs Phenomenon and Filtering ...................... 443
8.2. General Jacobi Polynomials in the Interval (—1,1) ... 445
The Jacobi Series. Truncation and Projection ........ 447
Gauss-Type Quadrature Formulas and Discrete Inner
Products ............................................ 448
Discrete Polynomial Transform and Interpolation ..... 449
Differentiation ..................................... 451
8.3. Chebyshev Polynomials ............................... 451
Quadrature Formulas and Discrete Transforms ......... 453
Differentiation ..................................... 454
8.4. Legendre Polynomials ................................ 455
Quadrature Formulas and Discrete Norms .............. 457
Differentiation ..................................... 457
8.5. Modal and Nodal Boundary-Adapted Bases on the
Interval ............................................ 458
8.6. Orthogonal Systems in Unbounded Domains ............. 460
Laguerre Polynomials and Laguerre Functions ......... 460
Hermite Polynomials and Hermite Functions ........... 461
8.7. Multidimensional Expansions ......................... 462
8.7.1. Tensor-Product Expansions ................... 463
8.7.2. Expansions on Simplicial Domains ............ 465
Collapsed Coordinates and Warped Tensor-
Product Expansions .......................... 465
Non- Tensor-Product Expansions .............. 468
8.8. Mappings ............................................ 468
8.8.1. Finite Intervals ............................ 469
8.8.2. Semi-Infinite Intervals ..................... 471
8.8.3. The Real Line ............................... 473
8.8.4. Multidimensional Mappings on Finite
Domains ..................................... 475
8.9. Basic Spectral Discretization Methods ............... 478
8.9.1. Tau Method .................................. 479
8.9.2. Collocation Method .......................... 481
8.9.3. Galerkin Method ............................. 482
8.9.4. Galerkin with Numerical Integration (G-NI)
Method ...................................... 484
8.9.5. Other Boundary Conditions ................... 485
Appendix A. Basic Mathematical Concepts ....................... 489
A.l. Hilbert and Banach Spaces ............................... 489
A.2. The Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality ........................... 491
A.3. The Lax-Milgram Theorem ................................. 492
A.4. Dense Subspace of a Normed Space ........................ 492
A.5. The Spaces .................................... 416
7.3.2. Conditioning and Preconditioning for the
Pressure Schur Complement Matrix ............ 419
7.3.3. Domain Decomposition Preconditioners for
the Stokes and Navier-Stokes Equations ...... 421
7.4. Algebraic Factorization Methods ..................... 425
7.4.1. Chorin-Temam and Yosida Algebraic
Factorization Methods ....................... 425
7.4.2. Numerical Results for Yosida Schemes ........ 428
7.4.3. Preconditioners for the Approximate
Pressure Schur Complement ................... 430
8. Spectral Methods Primer ................................... 435
8.1. The Fourier System .................................. 435
The Fourier Series .................................. 436
Truncation and Projection ........................... 436
Decay of the Fourier Coefficients ................... 437
Discrete Fourier Expansion and Interpolation ........ 438
Aliasing ............................................ 440
Differentiation ..................................... 441
Gibbs Phenomenon and Filtering ...................... 443
8.2. General Jacobi Polynomials in the Interval (—1,1) ... 445
The Jacobi Series. Truncation and Projection ........ 447
Gauss-Type Quadrature Formulas and Discrete Inner
Products ............................................ 448
Discrete Polynomial Transform and Interpolation ..... 449
Differentiation ..................................... 451
8.3. Chebyshev Polynomials ............................... 451
Quadrature Formulas and Discrete Transforms ......... 453
Differentiation ..................................... 454
8.4. Legendre Polynomials ................................ 455
Quadrature Formulas and Discrete Norms .............. 457
Differentiation ..................................... 457
8.5. Modal and Nodal Boundary-Adapted Bases on the
Interval ............................................ 458
8.6. Orthogonal Systems in Unbounded Domains ............. 460
Laguerre Polynomials and Laguerre Functions ......... 460
Hermite Polynomials and Hermite Functions ........... 461
8.7. Multidimensional Expansions ......................... 462
8.7.1. Tensor-Product Expansions ................... 463
8.7.2. Expansions on Simplicial Domains ............ 465
Collapsed Coordinates and Warped Tensor-
Product Expansions .......................... 465
Non- Tensor-Product Expansions .............. 468
8.8. Mappings ............................................ 468
8.8.1. Finite Intervals ............................ 469
8.8.2. Semi-Infinite Intervals ..................... 471
8.8.3. The Real Line ............................... 473
8.8.4. Multidimensional Mappings on Finite
Domains ..................................... 475
8.9. Basic Spectral Discretization Methods ............... 478
8.9.1. Tau Method .................................. 479
8.9.2. Collocation Method .......................... 481
8.9.3. Galerkin Method ............................. 482
8.9.4. Galerkin with Numerical Integration (G-NI)
Method ...................................... 484
8.9.5. Other Boundary Conditions ................... 485
Appendix A. Basic Mathematical Concepts ....................... 489
A.l. Hilbert and Banach Spaces ............................... 489
A.2. The Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality ........................... 491
A.3. The Lax-Milgram Theorem ................................. 492
A.4. Dense Subspace of a Normed Space ........................ 492
A.5. The Spaces 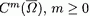 .................................. 493
A.6. The Spaces .................................. 493
A.6. The Spaces 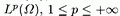 .............................. 493
A.7. Infinitely Differentiable Functions and Distributions ... 494
A.8. Sobolev Spaces and Sobolev Norms ........................ 496
A.9. The Sobolev Inequality .................................. 501
A.10. The Poincare Inequality ................................. 501
Appendix B. Fast Fourier Transforms ........................... 503
Appendix C. Iterative Methods for Linear Systems .............. 509
C.1. A Gentle Approach to Iterative Methods .................. 509
C.2. Descent Methods for Symmetric Problems .................. 513
C.3. Krylov Methods for Nonsymmetric Problems ................ 518
Appendix D. Time Discretizations .............................. 525
D.1. Notation and Stability Definitions ...................... 525
D.2. Standard ODE Methods .................................... 528
D.2.1. Leap Prog Method ................................. 529
D.2.2. Adams-Bashforth Methods .......................... 529
D.2.3. Adams-Moulton Methods ............................ 531
D.2.4. Backwards-Difference Formulas .................... 533
D.2.5. Runge-Kutta Methods .............................. 534
D.3. Low-Storage Schemes ...................................... 535
Appendix E. Supplementary Material ............................ 537
E.1. Numerical Solution of the Generalized Eigenvalue
Problem .................................................. 537
E.2. Tau Correction for the Kleiser-Schumann Method ........... 539
E.3. The Piola Transform ...................................... 541
References .................................................... 544 .............................. 493
A.7. Infinitely Differentiable Functions and Distributions ... 494
A.8. Sobolev Spaces and Sobolev Norms ........................ 496
A.9. The Sobolev Inequality .................................. 501
A.10. The Poincare Inequality ................................. 501
Appendix B. Fast Fourier Transforms ........................... 503
Appendix C. Iterative Methods for Linear Systems .............. 509
C.1. A Gentle Approach to Iterative Methods .................. 509
C.2. Descent Methods for Symmetric Problems .................. 513
C.3. Krylov Methods for Nonsymmetric Problems ................ 518
Appendix D. Time Discretizations .............................. 525
D.1. Notation and Stability Definitions ...................... 525
D.2. Standard ODE Methods .................................... 528
D.2.1. Leap Prog Method ................................. 529
D.2.2. Adams-Bashforth Methods .......................... 529
D.2.3. Adams-Moulton Methods ............................ 531
D.2.4. Backwards-Difference Formulas .................... 533
D.2.5. Runge-Kutta Methods .............................. 534
D.3. Low-Storage Schemes ...................................... 535
Appendix E. Supplementary Material ............................ 537
E.1. Numerical Solution of the Generalized Eigenvalue
Problem .................................................. 537
E.2. Tau Correction for the Kleiser-Schumann Method ........... 539
E.3. The Piola Transform ...................................... 541
References .................................................... 544
|
|