Preface to the Third Edition ................................... xi
1 Introduction ................................................. 1
1.1 Introductory Remarks .................................... 1
1.2 Turbulence - Miscellaneous Remarks ...................... 3
1.3 The Ubiquity of Turbulence .............................. 7
1.4 The Continuum Hypothesis ................................ 8
1.5 Measures of Turbulence - Intensity ..................... 11
1.6 Measures of Turbulence - Scale ......................... 14
1.7 Measures of Turbulence - The Energy Spectrum ........... 19
1.8 Measures of Turbulence - Intermittency ................. 22
1.9 The Diffusive Nature of Turbulence ..................... 23
1.10 Turbulence Simulation .................................. 26
References .................................................. 31
2 Conservation Equations for Compressible Turbulent Flows ..... 33
2.1 Introduction ........................................... 33
2.2 The Navier-Stokes Equations ............................ 34
2.3 Conventional Time-Averaging and Mass-Weighted-
Averaging Procedures ................................... 35
2.4 Relation Between Conventional Time-Averaged
Quantities and Mass-Weighted-Averaged Quantities ....... 39
2.5 Continuity and Momentum Equations ...................... 41
2.6 Energy Equations ....................................... 41
2.7 Mean-Kinetic-Energy Equation ........................... 42
2.8 Reynolds-Stress Transport Equations .................... 44
2.9 Reduced Forms of the Navier-Stokes Equations ........... 48
References .................................................. 51
3 Boundary-Layer Equations .................................... 53
3.1 Introduction ........................................... 54
3.2 Boundary-Layer Approximations for Compressible Flows ... 54
3.2.1 Laminar Flows ................................... 55
3.2.2 Turbulent Flows ................................. 59
3.3 Continuity, Momentum, and Energy Equations ............. 64
3.3.1 Two-Dimensional Flows ............................ 64
3.3.2 Axisymmetric Flows .............................. 69
3.3.3 Three-Dimensional Flows ......................... 71
3.4 Mean-Kinetic-Energy Flows .............................. 73
3.5 Reynolds-Stress Transport Equations .................... 74
3.6 Integral Equations of the Boundary Layer ............... 78
3.6.1 Momentum Integral Equation ...................... 79
3.6.2 Mean Energy Integral Equation ................... 80
3.6.3 Turbulent Energy Integral Equation .............. 81
3.6.4 Energy Integral Equation ........................ 82
References .................................................. 87
4 General Behavior of Turbulent Boundary Layers ............... 89
4.1 Introduction ........................................... 90
4.2 Composite Nature of a Turbulent Boundary Layer ......... 90
4.3 Eddy-Viscosity, Mixing-Length, Eddy-Conductivity and
Turbulent Prandtl Number Concepts ...................... 99
4.4 Mean-Velocity and Temperature Distributions in
Incompressible Flows on Smooth Surfaces ............... 104
4.4.1 Viscous and Conductive Sublayers ............... 107
4.4.2 Fully Turbulent Part of the Inner Region ....... 108
4.4.3 Inner Region ................................... 109
4.4.4 Outer Region ................................... 112
4.4.5 Equilibrium Boundary Layers .................... 116
4.4.6 Velocity and Temperature Distributions for
the Whole Layer Velocity Profile ............... 117
4.5 Mean-Velocity Distributions in Incompressible
Turbulent Flows on Rough Surfaces with Zero Pressure
Gradient .............................................. 123
4.6 Mean-Velocity Distribution on Smooth Porous Surfaces
with Zero Pressure Gradient ........................... 129
4.7 The Crocco Integral for Turbulent Boundary Layers ..... 131
4.8 Mean-Velocity and Temperature Distributions in
Compressible Flows with Zero Pressure Gradient ........ 135
4.8.1 The Law-of-the-Wall for Compressible Flows ..... 135
4.8.2 Van Driest Transformation for the Law of the
Wall ........................................... 139
4.8.3 Transformations for Compressible Turbulent
Flows .......................................... 140
4.8.4 Law of the Wall for Compressible Flow with
Mass Transfer .................................. 143
4.9 Effect of Pressure Gradient on Mean-Velocity and
Temperature Distributions in Incompressible and
Compressible Flows .................................... 145
References ................................................. 150
5 Algebraic Turbulence Models ................................ 155
5.1 Introduction .......................................... 156
5.2 Eddy Viscosity and Mixing Length Models ............... 156
5.3 CS Model .............................................. 160
5.3.1 Effect of Low Reynolds Number .................. 161
5.3.2 Effect of Transverse Curvature ................. 165
5.3.3 Effect of Streamwise Wall Curvature ............ 166
5.3.4 The Effect of Natural Transition ............... 168
5.3.5 Effect of Roughness ............................ 172
5.4 Extension of the CS Model to Strong Pressure-
Gradient Flows ........................................ 175
5.4.1 Johnson-King Approach .......................... 175
5.4.2 Cebeci-Chang Approach .......................... 178
5.5 Extensions of the CS Model to Navier-Stokes Methods ... 181
5.6 Eddy Conductivity and Turbulent Prandtl Number
Models ................................................ 185
5.7 CS Model for Three-Dimensional Flows .................. 194
5.7.1 Infinite Swept Wing Flows ...................... 196
5.7.2 Full Three-Dimensional Flows ................... 199
5.8 Summary ............................................... 203
References ................................................. 205
6 Transport-Equation Turbulence Models ....................... 211
6.1 Introduction .......................................... 211
6.2 Two-Equation Models ................................... 215
6.2.1 k-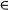 Model ...................................... 215
6.2.2 k-to Model ..................................... 221
6.2.3 SST Model ...................................... 224
6.3 One-Equation Models ................................... 226
6.3.1 Bradshaw's Model ............................... 227
6.3.2 Spalart-Allmaras Model ......................... 228
6.4 Stress-Transport Models ............................... 230
References ................................................. 235
7 Short Cut Methods .......................................... 237
7.1 Introduction .......................................... 238
7.2 Flows with Zero-Pressure Gradient ..................... 238
7.2.1 Incompressible Flow on a Smooth Flat Plate ..... 239
7.2.2 Incompressible Flow on a Rough Flat Plate ...... 248
7.2.3 Compressible Flow on a Smooth Flat Plate ....... 250
7.2.4 Compressible Flow on a Rough Flat Plate ........ 256
7.3 Flows with Pressure Gradient: Integral Methods ........ 257
7.4 Prediction of Flow Separation in Incompressible Flows . 264
7.5 Free Shear Flows ...................................... 268
7.5.1 Two-Dimensional Turbulent Jet .................. 268
7.5.2 Turbulent Mixing Layer Between Two Uniform
Streams at Different Temperatures .............. 273
7.5.3 Power Laws for the Width and the Centerline
Velocity of Similar Free Shear Layers .......... 280
Appendix 7A Gamma, Beta and Incomplete Beta Functions ...... 281
References ................................................. 291
8 Differential Methods with Algebraic Turbulence Models ...... 293
8.1 Introduction .......................................... 294
8.2 Numerical Solution of the Boundary-Layer Equations
with Algebraic Turbulence Models ...................... 295
8.2.1 Numerical Formulation .......................... 297
8.2.2 Newton's Method ................................ 299
8.2.3 Block-Elimination Method ....................... 301
8.2.4 Subroutine SOLV3 ............................... 302
8.3 Prediction of Two-Dimensional Incompressible Flows .... 305
8.3.1 Impermeable Surface with Zero Pressure
Gradient ....................................... 305
8.3.2 Permeable Surface with Zero Pressure Gradient .. 307
8.3.3 Impermeable Surface with Pressure Gradient ..... 310
8.3.4 Permeable Surface with Pressure Gradient ....... 312
8.4 Axisymmetric Incompressible Flows ..................... 315
8.5 Two-Dimensional Compressible Flows .................... 317
8.5.1 Impermeable Surface with Zero Pressure
Gradient ....................................... 317
8.5.2 Permeable Surface with Zero Pressure Gradient .. 320
8.5.3 Impermeable Surface with Pressure Gradient ..... 320
8.6 Axisymmetric Compressible Flows ....................... 322
8.7 Prediction of Two-Dimensional Incompressible Flows
with Separation ....................................... 322
8.7.1 Interaction Problem ............................. 324
8.8 Numerical Solution of the Boundary-Layer Equations
in the Inverse Mode with Algebraic Turbulence Models .. 326
8.8.1 Numerical Formulation ........................... 328
8.9 Hess-Smith (HS) Panel Method .......................... 333
8.9.1 Viscous Effects ................................ 340
8.9.2 Flowfield Calculation in the Wake .............. 342
8.10 Results for Airfoil Flows ............................. 344
8.11 Prediction of Three-Dimensional Flows with Separation . 347
References ................................................. 354
9 Differential Methods with Transport-Equation Turbulence
Models ..................................................... 357
9.1 Introduction .......................................... 358
9.2 Zonal Method for k- Model ...................................... 215
6.2.2 k-to Model ..................................... 221
6.2.3 SST Model ...................................... 224
6.3 One-Equation Models ................................... 226
6.3.1 Bradshaw's Model ............................... 227
6.3.2 Spalart-Allmaras Model ......................... 228
6.4 Stress-Transport Models ............................... 230
References ................................................. 235
7 Short Cut Methods .......................................... 237
7.1 Introduction .......................................... 238
7.2 Flows with Zero-Pressure Gradient ..................... 238
7.2.1 Incompressible Flow on a Smooth Flat Plate ..... 239
7.2.2 Incompressible Flow on a Rough Flat Plate ...... 248
7.2.3 Compressible Flow on a Smooth Flat Plate ....... 250
7.2.4 Compressible Flow on a Rough Flat Plate ........ 256
7.3 Flows with Pressure Gradient: Integral Methods ........ 257
7.4 Prediction of Flow Separation in Incompressible Flows . 264
7.5 Free Shear Flows ...................................... 268
7.5.1 Two-Dimensional Turbulent Jet .................. 268
7.5.2 Turbulent Mixing Layer Between Two Uniform
Streams at Different Temperatures .............. 273
7.5.3 Power Laws for the Width and the Centerline
Velocity of Similar Free Shear Layers .......... 280
Appendix 7A Gamma, Beta and Incomplete Beta Functions ...... 281
References ................................................. 291
8 Differential Methods with Algebraic Turbulence Models ...... 293
8.1 Introduction .......................................... 294
8.2 Numerical Solution of the Boundary-Layer Equations
with Algebraic Turbulence Models ...................... 295
8.2.1 Numerical Formulation .......................... 297
8.2.2 Newton's Method ................................ 299
8.2.3 Block-Elimination Method ....................... 301
8.2.4 Subroutine SOLV3 ............................... 302
8.3 Prediction of Two-Dimensional Incompressible Flows .... 305
8.3.1 Impermeable Surface with Zero Pressure
Gradient ....................................... 305
8.3.2 Permeable Surface with Zero Pressure Gradient .. 307
8.3.3 Impermeable Surface with Pressure Gradient ..... 310
8.3.4 Permeable Surface with Pressure Gradient ....... 312
8.4 Axisymmetric Incompressible Flows ..................... 315
8.5 Two-Dimensional Compressible Flows .................... 317
8.5.1 Impermeable Surface with Zero Pressure
Gradient ....................................... 317
8.5.2 Permeable Surface with Zero Pressure Gradient .. 320
8.5.3 Impermeable Surface with Pressure Gradient ..... 320
8.6 Axisymmetric Compressible Flows ....................... 322
8.7 Prediction of Two-Dimensional Incompressible Flows
with Separation ....................................... 322
8.7.1 Interaction Problem ............................. 324
8.8 Numerical Solution of the Boundary-Layer Equations
in the Inverse Mode with Algebraic Turbulence Models .. 326
8.8.1 Numerical Formulation ........................... 328
8.9 Hess-Smith (HS) Panel Method .......................... 333
8.9.1 Viscous Effects ................................ 340
8.9.2 Flowfield Calculation in the Wake .............. 342
8.10 Results for Airfoil Flows ............................. 344
8.11 Prediction of Three-Dimensional Flows with Separation . 347
References ................................................. 354
9 Differential Methods with Transport-Equation Turbulence
Models ..................................................... 357
9.1 Introduction .......................................... 358
9.2 Zonal Method for k-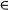 Model ............................ 358
9.2.1 Turbulence Equations and Boundary Conditions ... 359
9.2.2 Solution Procedure ............................. 360
9.3 Solution of the k- Model ............................ 358
9.2.1 Turbulence Equations and Boundary Conditions ... 359
9.2.2 Solution Procedure ............................. 360
9.3 Solution of the k-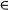 Model Equations with
and without Wall Functions ............................ 371
9.3.1 Solution of the k- Model Equations with
and without Wall Functions ............................ 371
9.3.1 Solution of the k-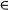 Model Equations without
Wall Functions ................................. 371
9.3.2 Solution of the k- Model Equations without
Wall Functions ................................. 371
9.3.2 Solution of the k-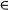 Model Equations with Wall
Functions ...................................... 374
9.4 Solution of the k-w and SST Model Equations ........... 375
9.5 Evaluation of Four Turbulence Models .................. 378
9.5.1 Free-Shear Flows ............................... 379
9.5.2 Attached and Separated Turbulent Boundary
Layers ......................................... 384
9.5.3 Summary ........................................ 389
9A. Appendix: Coefficients of the Linearized Finite-
Difference Equations for the k- Model Equations with Wall
Functions ...................................... 374
9.4 Solution of the k-w and SST Model Equations ........... 375
9.5 Evaluation of Four Turbulence Models .................. 378
9.5.1 Free-Shear Flows ............................... 379
9.5.2 Attached and Separated Turbulent Boundary
Layers ......................................... 384
9.5.3 Summary ........................................ 389
9A. Appendix: Coefficients of the Linearized Finite-
Difference Equations for the k-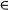 Model ................. 392
References ................................................. 407
10 Companion Computer Programs ................................ 409
10.1 Introduction .......................................... 411
10.2 Integral Methods ...................................... 412
10.2.1 Thwaites' Method ............................... 412
10.2.2 Smith-Spalding Method .......................... 412
10.2.3 Head's Method .................................. 412
10.2.4 Ambrok's Method ................................ 413
10.3 Differential Method with CS Model: Two-Dimensional
Laminar and Turbulent Flows ........................... 413
10.3.1 Main ........................................... 413
10.3.2 Subroutine INPUT ............................... 414
10.3.3 Subroutine IVPL ................................ 416
10.3.4 Subroutine GROWTH .............................. 417
10.3.5 Subroutine COEF3 ............................... 417
10.3.6 Subroutine EDDY ................................ 417
10.3.7 Subroutine SOLV3 ............................... 418
10.3.8 Subroutine OUTPUT .............................. 418
10.4 Hess-Smith Panel with Viscous Effects ................. 418
10.4.1 Main ........................................... 418
10.4.2 Subroutine COEF ................................ 419
10.4.3 Subroutine OBKUTA .............................. 419
10.4.4 Subroutine GAUSS ............................... 419
10.4.5 Subroutine VPDIS ............................... 419
10.4.6 Subroutine CLCM ................................ 420
10.4.7 Subroutine VPDWK ............................... 420
10.5 Differential Method with CS Model: Two-Dimensional
Flows with Heat Transfer .............................. 420
10.6 Differential Method with CS Model: Infinite Swept-
Wing Flows ............................................ 421
10.7 Differential Method with CS and k- Model ................. 392
References ................................................. 407
10 Companion Computer Programs ................................ 409
10.1 Introduction .......................................... 411
10.2 Integral Methods ...................................... 412
10.2.1 Thwaites' Method ............................... 412
10.2.2 Smith-Spalding Method .......................... 412
10.2.3 Head's Method .................................. 412
10.2.4 Ambrok's Method ................................ 413
10.3 Differential Method with CS Model: Two-Dimensional
Laminar and Turbulent Flows ........................... 413
10.3.1 Main ........................................... 413
10.3.2 Subroutine INPUT ............................... 414
10.3.3 Subroutine IVPL ................................ 416
10.3.4 Subroutine GROWTH .............................. 417
10.3.5 Subroutine COEF3 ............................... 417
10.3.6 Subroutine EDDY ................................ 417
10.3.7 Subroutine SOLV3 ............................... 418
10.3.8 Subroutine OUTPUT .............................. 418
10.4 Hess-Smith Panel with Viscous Effects ................. 418
10.4.1 Main ........................................... 418
10.4.2 Subroutine COEF ................................ 419
10.4.3 Subroutine OBKUTA .............................. 419
10.4.4 Subroutine GAUSS ............................... 419
10.4.5 Subroutine VPDIS ............................... 419
10.4.6 Subroutine CLCM ................................ 420
10.4.7 Subroutine VPDWK ............................... 420
10.5 Differential Method with CS Model: Two-Dimensional
Flows with Heat Transfer .............................. 420
10.6 Differential Method with CS Model: Infinite Swept-
Wing Flows ............................................ 421
10.7 Differential Method with CS and k-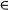 Models:
Components of the Computer Program Common to both
Models ................................................ 421
10.7.1 MAIN ........................................... 421
10.7.2 Subroutine INPUT ............................... 422
10.7.3 Subroutine IVPT ................................ 423
10.7.4 Subroutine GROWTH .............................. 423
10.7.5 Subroutine GRID ................................ 423
10.7.6 Subroutine OUTPUT .............................. 423
10.8 Differential Method with CS and k- Models:
Components of the Computer Program Common to both
Models ................................................ 421
10.7.1 MAIN ........................................... 421
10.7.2 Subroutine INPUT ............................... 422
10.7.3 Subroutine IVPT ................................ 423
10.7.4 Subroutine GROWTH .............................. 423
10.7.5 Subroutine GRID ................................ 423
10.7.6 Subroutine OUTPUT .............................. 423
10.8 Differential Method with CS and k-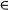 Models: CS Model .. 424
10.8.1 Subroutine COEFTR .............................. 424
10.8.2 Subroutine SOLV3 ............................... 424
10.8.3 Subroutines EDDY, GAMCAL, CALFA ................ 424
10.9 Differential Method with CS and k- Models: CS Model .. 424
10.8.1 Subroutine COEFTR .............................. 424
10.8.2 Subroutine SOLV3 ............................... 424
10.8.3 Subroutines EDDY, GAMCAL, CALFA ................ 424
10.9 Differential Method with CS and k-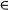 Models: k- Models: k-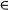 Model ................................................. 425
10.9.1 Subroutines KECOEF, KEPARM, KEDEF and KEDAMP ... 425
10.9.2 Subroutine KEINITK ............................. 427
10.9.3 Subroutine KEINITG ............................. 428
10.9.4 Subroutine KEWALL .............................. 428
10.9.5 Subroutine KESOLV .............................. 428
10.9.6 Test Cases for the CS and k-
Model ................................................. 425
10.9.1 Subroutines KECOEF, KEPARM, KEDEF and KEDAMP ... 425
10.9.2 Subroutine KEINITK ............................. 427
10.9.3 Subroutine KEINITG ............................. 428
10.9.4 Subroutine KEWALL .............................. 428
10.9.5 Subroutine KESOLV .............................. 428
10.9.6 Test Cases for the CS and k-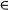 Models ........... 429
10.9.7 Solution Algorithm ............................. 429
10.10 Differential Method with CS and k- Models ........... 429
10.9.7 Solution Algorithm ............................. 429
10.10 Differential Method with CS and k-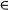 Models: Basic
Tools ................................................. 431
10.11 Differential Method with SA Model .................... 431
10.12 Differential Method for a Plane Jet .................. 432
10.13 Useful Subroutines ................................... 432
10.13.1 Subroutine IVPT ............................... 432
10.13.2 Subroutine SOLV2 .............................. 432
10.14 Differential Method for Inverse Boundary-Layer Flows
with CS Model ......................................... 432
10.14.1 Subroutine INPUT .............................. 433
10.14.2 Subroutine HIC ................................ 434
10.15 Comparison Computer Programs ......................... 435
10.15.1 Sample Calculations for the Panel Method
without Viscous Effects ....................... 435
10.15.2 Sample Calculations for the Inverse
Boundary-Layer Program ........................ 438
10.15.3 Sample Calculations with the Interactive
Boundary-Layer program ........................ 439
References ................................................. 446
Index ......................................................... 447 Models: Basic
Tools ................................................. 431
10.11 Differential Method with SA Model .................... 431
10.12 Differential Method for a Plane Jet .................. 432
10.13 Useful Subroutines ................................... 432
10.13.1 Subroutine IVPT ............................... 432
10.13.2 Subroutine SOLV2 .............................. 432
10.14 Differential Method for Inverse Boundary-Layer Flows
with CS Model ......................................... 432
10.14.1 Subroutine INPUT .............................. 433
10.14.2 Subroutine HIC ................................ 434
10.15 Comparison Computer Programs ......................... 435
10.15.1 Sample Calculations for the Panel Method
without Viscous Effects ....................... 435
10.15.2 Sample Calculations for the Inverse
Boundary-Layer Program ........................ 438
10.15.3 Sample Calculations with the Interactive
Boundary-Layer program ........................ 439
References ................................................. 446
Index ......................................................... 447
|