Part I Basic Mathematics
1 Basic Mathematical Background: Introduction .................. 3
1.1 Definition of a Group ................................... 3
1.2 Simple Example of a Group ............................... 3
1.3 Basic Definitions ....................................... 6
1.4 Rearrangement Theorem ................................... 7
1.5 Cosets .................................................. 7
1.6 Conjugation and Class ................................... 9
1.7 Factor Groups .......................................... 11
1.8 Group Theory and Quantum Mechanics ..................... 11
2 Representation Theory and Basic Theorems .................... 15
2.1 Important Definitions .................................. 15
2.2 Matrices ............................................... 16
2.3 Irreducible Representations ............................ 17
2.4 The Unitarity of Representations ....................... 19
2.5 Schur's Lemma (Part 1) ................................. 21
2.6 Schur's Lemma (Part 2) ................................. 23
2.7 Wonderful Orthogonality Theorem ........................ 25
2.8 Representations and Vector Spaces ...................... 28
3 Character of a Representation ............................... 29
3.1 Definition of Character ................................ 29
3.2 Characters and Class ................................... 30
3.3 Wonderful Orthogonality Theorem for Character .......... 31
3.4 Reducible Representations .............................. 33
3.5 The Number of Irreducible Representations .............. 35
3.6 Second Orthogonality Relation for Characters ........... 36
3.7 Regular Representation ................................. 37
3.8 Setting up Character Tables ............................ 40
3.9 Schoenflies Symmetry Notation .......................... 44
3.10 The Hermann-Mauguin Symmetry Notation .................. 46
3.11 Symmetry Relations and Point Group Classifications ..... 48
4 Basis Functions ............................................. 57
4.1 Symmetry Operations and Basis Functions ................ 57
4.2 Basis Functions for Irreducible Representations ........ 58
4.3 Projection Operators 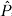 kl(Гn) ............................ 64
4.4 Derivation of an Explicit Expression for kl(Гn) ............................ 64
4.4 Derivation of an Explicit Expression for 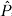 kℓ(Гn) ........ 64
4.5 The Effect of Projection Operations on an Arbitrary
Function ............................................... 65
4.6 Linear Combinations of Atomic Orbitals for Three
Equivalent Atoms at the Corners of an Equilateral
Triangle ............................................... 67
4.7 The Application of Group Theory to Quantum Mechanics ... 70
Part II Introductory Application to Quantum Systems
5 Splitting of Atomic Orbitals in a Crystal Potential ......... 79
5.1 Introduction ........................................... 79
5.2 Characters for the Full Rotation Group ................. 81
5.3 Cubic Crystal Field Environment for a Paramagnetic
Transition Metal Ion ................................... 85
5.4 Comments on Basis Functions ............................ 90
5.5 Comments on the Form of Crystal Fields ................. 92
6 Application to Selection Rules and Direct Products .......... 97
6.1 The Electromagnetic Interaction as a Perturbation ...... 97
6.2 Orthogonality of Basis Functions ....................... 99
6.3 Direct Product of Two Groups .......................... 100
6.4 Direct Product of Two Irreducible Representations ..... 101
6.5 Characters for the Direct Product ..................... 103
6.6 Selection Rule Concept in Group Theoretical Terms ..... 105
6.7 Example of Selection Rules ............................ 106
Part III Molecular Systems
7 Electronic States of Molecules and Directed Valence ........ 113
7.1 Introduction .......................................... 113
7.2 General Concept of Equivalence ........................ 115
7.3 Directed Valence Bonding .............................. 117
7.4 Diatomic Molecules .................................... 118
7.4.1 Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules ................. 118
7.4.2 Heterogeneous Diatomic Molecules ............... 120
7.5 Electronic Orbitals for Multiatomic Molecules ......... 124
7.5.1 The NH3 Molecule ............................... 124
7.5.2 The CH4 Molecule ............................... 125
7.5.3 The Hypothetical SH6 Molecule .................. 129
7.5.4 The Octahedral SF6 Molecule .................... 133
7.6 σ- and π-Bonds ....................................... 134
7.7 Jahn-Teller Effect .................................... 141
8 Molecular Vibrations, Infrared, and Raman Activity ......... 147
8.1 Molecular Vibrations: Background ...................... 147
8.2 Application of Group Theory to Molecular Vibrations ... 149
8.3 Finding the Vibrational Normal Modes .................. 152
8.4 Molecular Vibrations in H2O ........................... 154
8.5 Overtones and Combination Modes ....................... 156
8.6 Infrared Activity ..................................... 157
8.7 Raman Effect .......................................... 159
8.8 Vibrations for Specific Molecules ..................... 161
8.8.1 The Linear Molecules ........................... 161
8.8.2 Vibrations of the NH3 Molecule ................. 166
8.8.3 Vibrations of the CH4 Molecule ................. 168
8.9 Rotational Energy Levels .............................. 170
8.9.1 The Rigid Rotator .............................. 170
8.9.2 Wigner-Eckart Theorem .......................... 172
8.9.3 Vibrational-Rotational Interaction ............. 174
Part IV Application to Periodic Lattices
9 Space Groups in Real Space ................................. 183
9.1 Mathematical Background for Space Groups .............. 184
9.1.1 Space Groups Symmetry Operations ............... 184
9.1.2 Compound Space Group Operations ................ 186
9.1.3 Translation Subgroup ........................... 188
9.1.4 Symmorphic and Nonsymmorphic Space Groups ...... 189
9.2 Bravais Lattices and Space Groups ..................... 190
9.2.1 Examples of Symmorphic Space Groups ............ 192
9.2.2 Cubic Space Groups and the Equivalence
Transformation ................................. 194
9.2.3 Examples of Nonsymmorphic Space Groups ......... 196
9.3 Two-Dimensional Space Groups .......................... 198
9.3.1 2D Oblique Space Groups ........................ 200
9.3.2 2D Rectangular Space Groups .................... 201
9.3.3 2D Square Space Group .......................... 203
9.3.4 2D Hexagonal Space Groups ...................... 203
9.4 Line Groups ........................................... 204
9.5 The Determination of Crystal Structure and Space
Group ................................................. 205
9.5.1 Determination of the Crystal Structure ......... 206
9.5.2 Determination of the Space Group ............... 206
10 Space Groups in Reciprocal Space and Representations ....... 209
10.1 Reciprocal Space ...................................... 210
10.2 Translation Subgroup .................................. 211
10.2.1 Representations for the Translation Group ...... 211
10.2.2 Bloch's Theorem and the Basis of the
Translational Group ............................ 212
10.3 Symmetry of k Vectors and the Group of the Wave
Vector ................................................ 214
10.3.1 Point Group Operation in r-space and
k-space ........................................ 214
10.3.2 The Group of the Wave Vector Gk and the Star
of k ........................................... 215
10.3.3 Effect of Translations and Point Group
Operations on Bloch Functions .................. 215
10.4 Space Group Representations ........................... 219
10.4.1 Symmorphic Group Representations ............... 219
10.4.2 Nonsymmorphic Group Representations and the
Multiplier Algebra ............................. 220
10.5 Characters for the Equivalence Representation ......... 221
10.6 Common Cubic Lattices: Symmorphic Space Groups ........ 222
10.6.1 The Г Point .................................... 223
10.6.2 Points with k ≠ 0 .............................. 224
10.7 Compatibility Relations ............................... 227
10.8 The Diamond Structure: Nonsymmorphic Space Group ...... 230
10.8.1 Factor Group and the Г Point ................... 231
10.8.2 Points with k ≠ 0 .............................. 232
10.9 Finding Character Tables for all Groups of the Wave
Vector ................................................ 235
Part V Electron and Phonon Dispersion Relation
11 Applications to Lattice Vibrations ......................... 241
11.1 Introduction .......................................... 241
11.2 Lattice Modes and Molecular Vibrations ................ 244
11.3 Zone Center Phonon Modes .............................. 246
11.3.1 The NaCl Structure ............................. 246
11.3.2 The Perovskite Structure ....................... 247
11.3.3 Phonons in the Nonsymmorphic Diamond Lattice ... 250
11.3.4 Phonons in the Zinc Blende Structure ........... 252
11.4 Lattice Modes Away from k = 0 ......................... 253
11.4.1 Phonons in NaCl at the X Point k = (Π/α)
(100) ......................................... 254
11.4.2 Phonons in BaTiO3 at the X Point .............. 256
11.4.3 Phonons at the К Point in Two-Dimensional
Graphite ...................................... 258
11.5 Phonons in Те and α-Quartz Nonsymmorphic Structures ... 262
11.5.1 Phonons in Tellurium ........................... 262
11.5.2 Phonons in the α-Quartz Structure .............. 268
11.6 Effect of Axial Stress on Phonons ..................... 272
12 Electronic Energy Levels in a Cubic Crystals ............... 279
12.1 Introduction .......................................... 279
12.2 Plane Wave Solutions at k = 0 ......................... 282
12.3 Symmetrized Plane Solution Waves along the Δ-Axis ..... 286
12.4 Plane Wave Solutions at the X Point ................... 288
12.5 Effect of Glide Planes and Screw Axes ................. 294
13 Energy Band Models Based on Symmetry ....................... 305
13.1 Introduction .......................................... 305
13.2 k • p Perturbation Theory ............................. 307
13.3 Example of k • p Perturbation Theory for a
Nondegenerate Г1+ Band ................................. 308
13.4 Two Band Model: Degenerate First-Order Perturbation
Theory ................................................ 311
13.5 Degenerate second-order k • p Perturbation Theory ..... 316
13.6 Nondegenerate k • p Perturbation Theory at а Δ
Point ................................................. 324
13.7 Use of k • p Perturbation Theory to Interpret
Optical Experiments ................................... 326
13.8 Application of Group Theory to Valley-Orbit
Interactions in Semiconductors ........................ 327
13.8.1 Background ..................................... 328
13.8.2 Impurities in Multivalley Semiconductors ....... 330
13.8.3 The Valley-Orbit Interaction ................... 331
14 Spin-Orbit Interaction in Solids and Double Groups ......... 337
14.1 Introduction .......................................... 337
14.2 Crystal Double Groups ................................. 341
14.3 Double Group Properties ............................... 343
14.4 Crystal Field Splitting Including Spin-Orbit
Coupling .............................................. 349
14.5 Basis Functions for Double Group Representations ...... 353
14.6 Some Explicit Basis Functions ......................... 355
14.7 Basis Functions for Other Г8+ States .................. 358
14.8 Comments on Double Group Character Tables ............. 359
14.9 Plane Wave Basis Functions for Double Group
Representations ....................................... 360
14.10 Group of the Wave Vector for Nonsymmorphic Double
Groups ................................................ 362
15 Application of Double Groups to Energy Bands with Spin ..... 367
15.1 Introduction .......................................... 367
15.2 E(k) for the Empty Lattice Including Spin-Orbit
Interaction ........................................... 368
15.3 The k • p Perturbation with Spin-Orbit Interaction .... 369
15.4 E(k) for a Nondegenerate Band Including Spin-Orbit
Interaction ........................................... 372
15.5 E(k) for Degenerate Bands Including Spin-Orbit
Interaction ........................................... 374
15.6 Effective g-Factor .................................... 378
15.7 Fourier Expansion of Energy Bands: Slater-Koster
Method ................................................ 389
15.7.1 Contributions at d = 0 ......................... 396
15.7.2 Contributions at d = 1 ......................... 396
15.7.3 Contributions at d = 2 ......................... 397
15.7.4 Summing Contributions through d = 2 ............ 397
15.7.5 Other Degenerate Levels ........................ 397
Part VI Other Symmetries
16 Time Reversal Symmetry ..................................... 403
16.1 The Time Reversal Operator ............................ 403
16.2 Properties of the Time Reversal Operator .............. 404
16.3 The Effect of kℓ(Гn) ........ 64
4.5 The Effect of Projection Operations on an Arbitrary
Function ............................................... 65
4.6 Linear Combinations of Atomic Orbitals for Three
Equivalent Atoms at the Corners of an Equilateral
Triangle ............................................... 67
4.7 The Application of Group Theory to Quantum Mechanics ... 70
Part II Introductory Application to Quantum Systems
5 Splitting of Atomic Orbitals in a Crystal Potential ......... 79
5.1 Introduction ........................................... 79
5.2 Characters for the Full Rotation Group ................. 81
5.3 Cubic Crystal Field Environment for a Paramagnetic
Transition Metal Ion ................................... 85
5.4 Comments on Basis Functions ............................ 90
5.5 Comments on the Form of Crystal Fields ................. 92
6 Application to Selection Rules and Direct Products .......... 97
6.1 The Electromagnetic Interaction as a Perturbation ...... 97
6.2 Orthogonality of Basis Functions ....................... 99
6.3 Direct Product of Two Groups .......................... 100
6.4 Direct Product of Two Irreducible Representations ..... 101
6.5 Characters for the Direct Product ..................... 103
6.6 Selection Rule Concept in Group Theoretical Terms ..... 105
6.7 Example of Selection Rules ............................ 106
Part III Molecular Systems
7 Electronic States of Molecules and Directed Valence ........ 113
7.1 Introduction .......................................... 113
7.2 General Concept of Equivalence ........................ 115
7.3 Directed Valence Bonding .............................. 117
7.4 Diatomic Molecules .................................... 118
7.4.1 Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules ................. 118
7.4.2 Heterogeneous Diatomic Molecules ............... 120
7.5 Electronic Orbitals for Multiatomic Molecules ......... 124
7.5.1 The NH3 Molecule ............................... 124
7.5.2 The CH4 Molecule ............................... 125
7.5.3 The Hypothetical SH6 Molecule .................. 129
7.5.4 The Octahedral SF6 Molecule .................... 133
7.6 σ- and π-Bonds ....................................... 134
7.7 Jahn-Teller Effect .................................... 141
8 Molecular Vibrations, Infrared, and Raman Activity ......... 147
8.1 Molecular Vibrations: Background ...................... 147
8.2 Application of Group Theory to Molecular Vibrations ... 149
8.3 Finding the Vibrational Normal Modes .................. 152
8.4 Molecular Vibrations in H2O ........................... 154
8.5 Overtones and Combination Modes ....................... 156
8.6 Infrared Activity ..................................... 157
8.7 Raman Effect .......................................... 159
8.8 Vibrations for Specific Molecules ..................... 161
8.8.1 The Linear Molecules ........................... 161
8.8.2 Vibrations of the NH3 Molecule ................. 166
8.8.3 Vibrations of the CH4 Molecule ................. 168
8.9 Rotational Energy Levels .............................. 170
8.9.1 The Rigid Rotator .............................. 170
8.9.2 Wigner-Eckart Theorem .......................... 172
8.9.3 Vibrational-Rotational Interaction ............. 174
Part IV Application to Periodic Lattices
9 Space Groups in Real Space ................................. 183
9.1 Mathematical Background for Space Groups .............. 184
9.1.1 Space Groups Symmetry Operations ............... 184
9.1.2 Compound Space Group Operations ................ 186
9.1.3 Translation Subgroup ........................... 188
9.1.4 Symmorphic and Nonsymmorphic Space Groups ...... 189
9.2 Bravais Lattices and Space Groups ..................... 190
9.2.1 Examples of Symmorphic Space Groups ............ 192
9.2.2 Cubic Space Groups and the Equivalence
Transformation ................................. 194
9.2.3 Examples of Nonsymmorphic Space Groups ......... 196
9.3 Two-Dimensional Space Groups .......................... 198
9.3.1 2D Oblique Space Groups ........................ 200
9.3.2 2D Rectangular Space Groups .................... 201
9.3.3 2D Square Space Group .......................... 203
9.3.4 2D Hexagonal Space Groups ...................... 203
9.4 Line Groups ........................................... 204
9.5 The Determination of Crystal Structure and Space
Group ................................................. 205
9.5.1 Determination of the Crystal Structure ......... 206
9.5.2 Determination of the Space Group ............... 206
10 Space Groups in Reciprocal Space and Representations ....... 209
10.1 Reciprocal Space ...................................... 210
10.2 Translation Subgroup .................................. 211
10.2.1 Representations for the Translation Group ...... 211
10.2.2 Bloch's Theorem and the Basis of the
Translational Group ............................ 212
10.3 Symmetry of k Vectors and the Group of the Wave
Vector ................................................ 214
10.3.1 Point Group Operation in r-space and
k-space ........................................ 214
10.3.2 The Group of the Wave Vector Gk and the Star
of k ........................................... 215
10.3.3 Effect of Translations and Point Group
Operations on Bloch Functions .................. 215
10.4 Space Group Representations ........................... 219
10.4.1 Symmorphic Group Representations ............... 219
10.4.2 Nonsymmorphic Group Representations and the
Multiplier Algebra ............................. 220
10.5 Characters for the Equivalence Representation ......... 221
10.6 Common Cubic Lattices: Symmorphic Space Groups ........ 222
10.6.1 The Г Point .................................... 223
10.6.2 Points with k ≠ 0 .............................. 224
10.7 Compatibility Relations ............................... 227
10.8 The Diamond Structure: Nonsymmorphic Space Group ...... 230
10.8.1 Factor Group and the Г Point ................... 231
10.8.2 Points with k ≠ 0 .............................. 232
10.9 Finding Character Tables for all Groups of the Wave
Vector ................................................ 235
Part V Electron and Phonon Dispersion Relation
11 Applications to Lattice Vibrations ......................... 241
11.1 Introduction .......................................... 241
11.2 Lattice Modes and Molecular Vibrations ................ 244
11.3 Zone Center Phonon Modes .............................. 246
11.3.1 The NaCl Structure ............................. 246
11.3.2 The Perovskite Structure ....................... 247
11.3.3 Phonons in the Nonsymmorphic Diamond Lattice ... 250
11.3.4 Phonons in the Zinc Blende Structure ........... 252
11.4 Lattice Modes Away from k = 0 ......................... 253
11.4.1 Phonons in NaCl at the X Point k = (Π/α)
(100) ......................................... 254
11.4.2 Phonons in BaTiO3 at the X Point .............. 256
11.4.3 Phonons at the К Point in Two-Dimensional
Graphite ...................................... 258
11.5 Phonons in Те and α-Quartz Nonsymmorphic Structures ... 262
11.5.1 Phonons in Tellurium ........................... 262
11.5.2 Phonons in the α-Quartz Structure .............. 268
11.6 Effect of Axial Stress on Phonons ..................... 272
12 Electronic Energy Levels in a Cubic Crystals ............... 279
12.1 Introduction .......................................... 279
12.2 Plane Wave Solutions at k = 0 ......................... 282
12.3 Symmetrized Plane Solution Waves along the Δ-Axis ..... 286
12.4 Plane Wave Solutions at the X Point ................... 288
12.5 Effect of Glide Planes and Screw Axes ................. 294
13 Energy Band Models Based on Symmetry ....................... 305
13.1 Introduction .......................................... 305
13.2 k • p Perturbation Theory ............................. 307
13.3 Example of k • p Perturbation Theory for a
Nondegenerate Г1+ Band ................................. 308
13.4 Two Band Model: Degenerate First-Order Perturbation
Theory ................................................ 311
13.5 Degenerate second-order k • p Perturbation Theory ..... 316
13.6 Nondegenerate k • p Perturbation Theory at а Δ
Point ................................................. 324
13.7 Use of k • p Perturbation Theory to Interpret
Optical Experiments ................................... 326
13.8 Application of Group Theory to Valley-Orbit
Interactions in Semiconductors ........................ 327
13.8.1 Background ..................................... 328
13.8.2 Impurities in Multivalley Semiconductors ....... 330
13.8.3 The Valley-Orbit Interaction ................... 331
14 Spin-Orbit Interaction in Solids and Double Groups ......... 337
14.1 Introduction .......................................... 337
14.2 Crystal Double Groups ................................. 341
14.3 Double Group Properties ............................... 343
14.4 Crystal Field Splitting Including Spin-Orbit
Coupling .............................................. 349
14.5 Basis Functions for Double Group Representations ...... 353
14.6 Some Explicit Basis Functions ......................... 355
14.7 Basis Functions for Other Г8+ States .................. 358
14.8 Comments on Double Group Character Tables ............. 359
14.9 Plane Wave Basis Functions for Double Group
Representations ....................................... 360
14.10 Group of the Wave Vector for Nonsymmorphic Double
Groups ................................................ 362
15 Application of Double Groups to Energy Bands with Spin ..... 367
15.1 Introduction .......................................... 367
15.2 E(k) for the Empty Lattice Including Spin-Orbit
Interaction ........................................... 368
15.3 The k • p Perturbation with Spin-Orbit Interaction .... 369
15.4 E(k) for a Nondegenerate Band Including Spin-Orbit
Interaction ........................................... 372
15.5 E(k) for Degenerate Bands Including Spin-Orbit
Interaction ........................................... 374
15.6 Effective g-Factor .................................... 378
15.7 Fourier Expansion of Energy Bands: Slater-Koster
Method ................................................ 389
15.7.1 Contributions at d = 0 ......................... 396
15.7.2 Contributions at d = 1 ......................... 396
15.7.3 Contributions at d = 2 ......................... 397
15.7.4 Summing Contributions through d = 2 ............ 397
15.7.5 Other Degenerate Levels ........................ 397
Part VI Other Symmetries
16 Time Reversal Symmetry ..................................... 403
16.1 The Time Reversal Operator ............................ 403
16.2 Properties of the Time Reversal Operator .............. 404
16.3 The Effect of 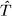 on E(k), Neglecting Spin .............. 407
16.4 The Effect of on E(k), Neglecting Spin .............. 407
16.4 The Effect of 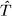 on E(k), Including the Spin-Orbit
Interaction ........................................... 411
16.5 Magnetic Groups ....................................... 416
16.5.1 Introduction ................................... 418
16.5.2 Types of Elements .............................. 418
16.5.3 Types of Magnetic Point Groups ................. 419
16.5.4 Properties of the 58 Magnetic Point Groups
{Ai, Mk} ....................................... 419
16.5.5 Examples of Magnetic Structures ................ 423
16.5.6 Effect of Symmetry on the Spin Hamiltonian
for the 32 Ordinary Point Groups ............... 426
17 Permutation Groups and Many-Electron States ................ 431
17.1 Introduction .......................................... 432
17.2 Classes and Irreducible Representations of
Permutation Groups .................................... 434
17.3 Basis Functions of Permutation Groups ................. 437
17.4 Pauli Principle in Atomic Spectra ..................... 440
17.4.1 Two-Electron States ............................ 440
17.4.2 Three-Electron States .......................... 443
17.4.3 Four-Electron States ........................... 448
17.4.4 Five-Electron States ........................... 451
17.4.5 General Comments on Many-Electron States ....... 451
18 Symmetry Properties of Tensors ............................. 455
18.1 Introduction .......................................... 455
18.2 Independent Components of Tensors Under Permutation
Group Symmetry ........................................ 458
18.3 Independent Components of Tensors: Point Symmetry
Groups ................................................ 462
18.4 Independent Components of Tensors Under Full
Rotational Symmetry ................................... 463
18.5 Tensors in Nonlinear Optics ........................... 463
18.5.1 Cubic Symmetry: Oh ............................. 464
18.5.2 Tetrahedral Symmetry: Td ....................... 466
18.5.3 Hexagonal Symmetry: D6h ........................ 466
18.6 Elastic Modulus Tensor ................................ 467
18.6.1 Full Rotational Symmetry: 3D Isotropy .......... 469
18.6.2 Icosahedral Symmetry ........................... 472
18.6.3 Cubic Symmetry ................................. 472
18.6.4 Other Symmetry Groups .......................... 474
A Point Group Character Tables ............................... 479
В Two-Dimensional Space Groups ............................... 489
С Tables for 3D Space Groups ................................. 499
C.l Real Space ............................................ 499
C.2 Reciprocal Space ...................................... 503
D Tables for Double Groups ................................... 521
E Group Theory Aspects of Carbon Nanotubes ................... 533
E.l Nanotube Geometry and the (n, m) Indices .............. 534
E.2 Lattice Vectors in Real Space ......................... 534
E.3 Lattice Vectors in Reciprocal Space ................... 535
E.4 Compound Operations and Tube Helicity ................. 536
E.5 Character Tables for Carbon Nanotubes ................. 538
F Permutation Group Character Tables ......................... 543
References ................................................. 549
Index ......................................................... 553 on E(k), Including the Spin-Orbit
Interaction ........................................... 411
16.5 Magnetic Groups ....................................... 416
16.5.1 Introduction ................................... 418
16.5.2 Types of Elements .............................. 418
16.5.3 Types of Magnetic Point Groups ................. 419
16.5.4 Properties of the 58 Magnetic Point Groups
{Ai, Mk} ....................................... 419
16.5.5 Examples of Magnetic Structures ................ 423
16.5.6 Effect of Symmetry on the Spin Hamiltonian
for the 32 Ordinary Point Groups ............... 426
17 Permutation Groups and Many-Electron States ................ 431
17.1 Introduction .......................................... 432
17.2 Classes and Irreducible Representations of
Permutation Groups .................................... 434
17.3 Basis Functions of Permutation Groups ................. 437
17.4 Pauli Principle in Atomic Spectra ..................... 440
17.4.1 Two-Electron States ............................ 440
17.4.2 Three-Electron States .......................... 443
17.4.3 Four-Electron States ........................... 448
17.4.4 Five-Electron States ........................... 451
17.4.5 General Comments on Many-Electron States ....... 451
18 Symmetry Properties of Tensors ............................. 455
18.1 Introduction .......................................... 455
18.2 Independent Components of Tensors Under Permutation
Group Symmetry ........................................ 458
18.3 Independent Components of Tensors: Point Symmetry
Groups ................................................ 462
18.4 Independent Components of Tensors Under Full
Rotational Symmetry ................................... 463
18.5 Tensors in Nonlinear Optics ........................... 463
18.5.1 Cubic Symmetry: Oh ............................. 464
18.5.2 Tetrahedral Symmetry: Td ....................... 466
18.5.3 Hexagonal Symmetry: D6h ........................ 466
18.6 Elastic Modulus Tensor ................................ 467
18.6.1 Full Rotational Symmetry: 3D Isotropy .......... 469
18.6.2 Icosahedral Symmetry ........................... 472
18.6.3 Cubic Symmetry ................................. 472
18.6.4 Other Symmetry Groups .......................... 474
A Point Group Character Tables ............................... 479
В Two-Dimensional Space Groups ............................... 489
С Tables for 3D Space Groups ................................. 499
C.l Real Space ............................................ 499
C.2 Reciprocal Space ...................................... 503
D Tables for Double Groups ................................... 521
E Group Theory Aspects of Carbon Nanotubes ................... 533
E.l Nanotube Geometry and the (n, m) Indices .............. 534
E.2 Lattice Vectors in Real Space ......................... 534
E.3 Lattice Vectors in Reciprocal Space ................... 535
E.4 Compound Operations and Tube Helicity ................. 536
E.5 Character Tables for Carbon Nanotubes ................. 538
F Permutation Group Character Tables ......................... 543
References ................................................. 549
Index ......................................................... 553
|